Mental / Emotional Health
(middle grades)
Unit, Activities and Lesson plans
- Overview
- Health standards, concepts, & outcomes
- Mental emotional health big ideas, concepts, & outcomes
- Decision making big ideas, concepts, & outcomes
- Pedagogical overview
- Unit activities sequence
- Resources and materials
- Scoring guide suggestions
- Lesson plans
- Lab Notes for activities
- Fact Sheets
- Setting and achieving goals
- Characteristics of humans
- Emotional Health Characteristics
- Maslow's Hierarchy
- Procedures to Manage Emotions:
- Recognize your feelings as emotionally related & defense mechanisms
- How to Increase Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
- Recognize your feelings as emotionally related & defense mechanisms
- Procedure to Manage Fear
- Procedure to Manage Guilt
- Procedure to Manage Anger
- Procedure to Manage and Deal with Stressful Situations
- Procedure for Refusal skills
- Coping with loss and grief: Five Stages of grief or loss
- Dealing with Anxiety and Depression
- Suicide Prevention and Getting Help
- Teen Stressors
- Bodily Responses to alarm, stress and chronic stress
- Ways to Manage and Reduce stress
- Exercise, hormones, and stress
- Hormones & other substances related to stress
- Immunity and exercise
- Caffeine and hormones
- Word bank
- References
- Review
- Review with answer key
Overview
This unit includes activities for students to develop a plan to maintain and improve their mental social and emotional health. It reviews social and emotional health: beneficial and detrimental behaviors and their effects on health and how influences impact decisions people make that promote or risk health and wellness. Decisions, often made subconsciously and emotionally without sufficient critical thinking.
Activities include: A two week goal setting activity, Identify a Media Character's Mental Health, Exploration of what is human, Study emotional health characteristics, Investigating: Who I am by making a coat of arms, Explore emotional health categories, Review Maslow's needs, self-esteem, self-efficacy, managing emotions, stress, exercise, loss, grief, anxiety, depression, and suicide prevention. and create a plan for a healthy social emotional life.
Background information:
This plan is designed as an introductory emotional and mental health investigation for middle level students. No background information, other than being middle level age, is necessary.
Social health is important for mental and emotional health and is referenced in this unit. However, the unit Social health and relationships is planned to follow this unit and will explore it in greater detail.
Related study topics:
- Investigate psychology and sociology topics.
- Related trade books for able readers
Additional study topics included in this middle school curriculum:
Big ideas, concepts, facts, and outcomes
Health standards
Big ideas and specific outcomes:
- Standard 1 - Comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health.
- Standard 2 - Analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behaviors.
- Standard 3 - Demonstrate the ability to access valid information and products and services to enhance health.
- Standard 4 - Demonstrate the ability to use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks.
- Standard 5 - Demonstrate the ability to use decision-making skills to enhance health.
- Standard 6 - Demonstrate the ability to use goal-setting skills to enhance health.
- Standard 7 - Demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce risks.
- Standard 8 - Demonstrate the ability to advocate for personal, family, and community health.
Related concepts
Big idea: Mental and emotional health is achieved with accurate information and a reasoned decision making process to choose actions and behaviors that facilitate health and wellness.
- Mental / emotional health is a state of emotional / mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals that cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Each person is responsible to management their behaviors and habits to maintain their health and wellness.
- Self-management is the decisions a person makes about diet, exercise, safety, first aid, seat belt usage, cell phone use, texting and driving, alcohol, medicine use, drug use, risk management, and any other behavioral choice that affects a person's health and wellness.
- People make better decisions when they use accurate information and consider factual verifiable information for the positive and negative effects of mental and emotional health.
- People make better decision when they understand and consider the positive and negative influences that effect their decision making.
Outcome
Use accurate verifiable information to consider health choices and influences when making decisions to manage health and wellness.
Mental & emotional health and wellness
Big ideas: Understanding how people maintain and improve their mental and emotional health can help improve theirs and others mental and emotional health and quality of life.
Related concepts
- The more a person knows about health and wellness, them self as an individual, and the different effects of their actions the better decisions they will make.
Outcome
- Describe positive and negative effects different mental and emotional behaviors and choices have on the human body.
- Describe processes of how different mental and emotional behaviors and choices interact with different body systems, tissues, and cells to result in healthy and unhealthy consequences.
Specific outcomes -
1.12.1 Predict how healthy behaviors can impact mental / emotional health status.
1.12.2 Describe the interrelationships of emotional, intellectual, physical, and social health with respect to mental health.
1.12.3 Analyze how environmental (social & physical effects) and personal health (mental / emotional) are interrelated.
1.12.4 Analyze how genetics and family history can impact personal health (mental / emotional).
1.12.5 Propose ways to reduce or prevent injuries and health problems (mental / emotional).
1.12.6 Analyze the relationship between access to health care and health status (mental / emotional).
1.12.7 Compare and contrast the benefits of and barriers to practicing a variety of healthy behaviors as related to mental / emotional health and wellness.
1.12.8 Analyze personal susceptibility to injury, illness, or death if engaging in unhealthy behaviors related to mental / emotional health and wellness.
1.12.9 Analyze the potential severity of injury or illness if engaging in unhealthy behaviors.
Decision-making skills to enhance health.
Big ideas: It is important to know how to discover accurate verifiable information about different behaviors to make good healthy decisions. Decision-making skills are necessary to identify, implement, and sustain health-enhancing behaviors. This includes essential steps needed to make healthy decisions applied to mental / emotional health, safety, and social issues to enable people to individually or in collaboration with others improve people's health and wellness and quality of life.
Related conceptsv
- Health and safety problems are related to decision making.
- The better a person knows them self, the better decisions they will make.
- Effective social skills improve communication and getting along with people.
- Thinking about a problem before experiencing it helps make better decisions.
- There are positive and negative consequences for all decisions.
- There are positive and negative influences to consider when making decisions.
Outcome
- Describe the relationships between making good decisions and being healthy.
- Describe a decision making process that includes identification of a problem, alternative solutions with positive and negative consequences, and implementation suggestions.
- Describe positive and negative influences that impact decision making.
- Use a decision making process to make safe and healthy decisions that improve people's quality of life.
Specific outcomes -
2.12.1 Analyze how family influences the health of individuals.
2.12.2 Analyze how culture supports and challenges health beliefs, practices, and behaviors.
2.12.3 Analyze how peers influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.4 Evaluate how the school and community can impact personal health practice and behaviors.
2.12.5 Evaluate the effect of media on personal and family health.
2.12.6 Evaluate the impact of technology on personal, family, and community health.
2.12.7 Analyze how the perceptions of norms influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.8 Analyze the influence of personal values and beliefs on individual health practices and behaviors.
2.12.9 Analyze how some health risk behaviors can influence the likelihood of engaging in unhealthy behaviors.
2.12.10 Analyze how public health policies and government regulations can influence health promotion and disease prevention
3.12.1 Evaluate the validity of health information, products, and services.
3.12.2 Utilize resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information.
3.12.3 Determine the accessibility of products and services that enhance health.
3.12.4 Determine when professional health services may be required.
3.12.5 Access valid and reliable health products and services.
4.12.1 Utilize skills for communicating effectively with family, peers, and others to enhance health.
4.12.2 Demonstrate refusal, negotiation, and collaboration skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks.
4.12.3 Demonstrate strategies to prevent, manage, or resolve interpersonal conflicts without harming self or others.
4.12.4 Demonstrate how to ask for and offer assistance to enhance the health of self and others.
5.12.1 Examine barriers that can hinder healthy decision making.
5.12.2 Determine the value of applying a thoughtful decision-making process in health-related situations.
5.12.3 Justify when individual or collaborative decision making is appropriate.
5.12.4 Generate alternatives to health-related issues or problems.
5.12.5 Predict the potential short and long term impact of each alternative on self and others.
5.12.6 Defend the healthy choice when making decisions.
5.12.7 Evaluate the effectiveness of health related decisions.
Pedagogical Overview
Unit activities sequence to provide sufficient opportunities for students to achieve the outcomes.
Lesson plans:
- Activity 1 - Setting and achieving a goal for two weeks
- Activity 2 - What's your Character's Mental Health? - Define characteristics of mental health and use them to determine the mental health of a fictional character in a story or series.
- Activity 3 - What is Human?
- Activity 4 - Who am I? - Create a personal shield or coat of arms that describes who you are.
- Activity 5 - Effects on health, risks and promoting health and wellness -
- Activity 6 - Investigate mental social emotional health -
- Activity 7 - Cross word puzzle for key words - in word bank
- Activity 8 - Create an action plan for social emotional health and wellness - Maslow's Hierarchy of needs, Stress, & Emotions (self-efficacy, fear, guilt, anger, grief, anxiety, & depression)
- Activity 9 - Review
Focus question
Unit focus question:
What can people do to maintain and improve their emotional and mental health?
Sub focus questions:
- What is emotional and mental health?
- What do people need to know to maintain and improve good emotional and mental health and wellness?
Resources and Materials
- Setting and achieving goals for two weeks
- Analyze a fictional character's mental health
- What's human?
- Who am I?
- Effects on health, risks and promoting health and wellness
- Mental and Emotional Vocabulary Crossword Puzzles - 1. Warm-up, 2. Expert, 3. Comprehensive
- Investigate mental and emotional health lab notes - Maslow's Hierarchy of needs, Stress, & Emotions (self-efficacy, fear, guilt, anger, grief, anxiety, & depression)
- Create an action plan for healthy emotional and mental life
- Activity 9 - Review - External page
- Review answer key - External page
- Setting and achieving goals
- Characteristics of humans
- Emotional Health Categories
- Maslow's Hierarchy
- Procedures to Manage Emotions:
- Recognize your feelings as emotionally related & defense mechanisms
- How to Increase Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
- Procedure to Manage Fear
- Procedure to Manage Guilt
- Procedure to Manage Anger
- Procedure to Manage and Deal with Stressful Situations
- Procedure for Refusal skills
- Teen Stressors
- Bodily Responses to alarm, stress and chronic stress
- Ways to Manage and Reduce stress
- Exercise, hormones, and stress
- Hormones and other substances related to stress, rest, and recovery
- Immunity and exercise
- Caffeine and hormones
- Coping with loss and grief: Five Stages of grief or loss
- Dealing with Anxiety and Depression
- Suicide Prevention and Getting Help
Scoring guides suggestions (rubric)
Decision making with critical thinking to enhance health (scoring guide)
Top level:
- Uses critical thinking to make decisions with a process that includes focus on a process, accurate information, identification of a problem or opportunity, analysis, generation of alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, implementation, and evaluation suggestions and describes benefits for a comprehensive decision making process.
- Uses critical thinking to make decisions with a process that includes identification of a problem, alternative solutions with positive and negative consequences, and implementation suggestions and describes benefits for a comprehensive decision making process.
- Makes decisions with a multiple step process that uses several appropriate steps for making decisions and excludes some that may be necessary to make better critical decisions.
- Makes decisions subconsciously and emotionally or in a manner that believes will result in the best rewards personally, socially (parents, teachers, friends, ...)
Bottom level:
Social interactions in a conflict situation (scoring guide)
Top level
- Upper level: Social interactions recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences and identify multiple ways to resolve conflict with respect to accept each person's individual rights or assertion, and use appropriate social skills when focusing on and stating the problem, analyzing the problem, stating alternative options and choices with positive and negative consequences, and communicating decisions that most individuals accept.
- Middle level: Social interactions seem to recognize a conflict between subconscious influences and logical consequences while recognizing different ways to resolve conflict and attempt to solve problems with regard to individual rights of assertion and use of applicable social skills to make or accept a decision that most individuals can accept.
- Low level: Social interactions seem to be driven by subconscious emotional influences in a manner that suggests decisions are based on influences for immediate personal or social outcomes and rewards, without regard to individual rights, concern for conflict resolution, or use of applicable social skills.
Lower level
The rubrics were created based on the Healthy Practices Skills and Outcomes for a middle level health course, which were heavily influenced by the national health standards.
Lesson Plans
Two Week Setting and Achieving a Goal Activity (1)
Materials:
Focus questions:
- How do you get things done?
- How do you achieve what you want to do?
- How do you plan and achieve what you want to do?
Learning outcomes:
- Set and achieve a goal for a period of two weeks.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Ask focus questions.
- Share goal setting fact sheet.
- Students select something they may have previously consider doing or something new to set as a goal.
- Students fill out a goal setting lab sheet.
- Put students in pairs, have them review each others goal activity.
Scoring guide for goal setting and achieving activity
Top level
- Writes a goal, outlines a procedure to achieve it, monitor progress, and achieves it for fourteen days.
- Writes a goal, outlines a procedure to achieve it, monitor progress, and achieves it for less than thirteen days.
- Writes a goal, outlines a procedure to achieve it, monitor progress, and achieves it for twelve days.
- Writes a goal, outlines a procedure to achieve it, monitor progress, and achieves it less than twelve days.
Lower level
Exploration
Goal setting
- How do you get things done? Accept all answers and put them on a board for all to view.
- How do you achieve what you want to do?Accept all answers and put them on a board for all to view. How do you plan and achieve what you want to do? Accept all answers.
Invention
Set goals for learning
- If students haven't mentioned, goals, then introduce the term.
- Share the fact sheet for setting and achieving goals.
- Ask. Can you follow a procedure like the one on the fact sheet? Sort of.
- Ask. Are there other ideas that could help them achieve more of their goals. Add appropriate ideas to the goal procedure sheet.
- Tell. Goals are usually achieved with a process like this. Four step procedure or what was developed by the class.
- Tell. Think of a daily goal you could achieve each day for two weeks. Something you may have previously thought about doing or something new to set as a goal.
Examples:
- Walk / jog for 20 minutes each day.
- Practice an instrument for at least 20 minutes each day.
- Shoot 100 free throws a day. or Hit a softball 100 times each day.
- Clean the kitchen every night.
- Help someone with something they need or want to do each day.
- Write in a journal for at least 20 minutes each day.
- Read for at least 20 minutes each night.
- Give each student a Goal Setting lab notes page.
- Tell. Fill out the top part of the fact sheet.
- Put students in buddy pairs.
- Tell them to review each others goal setting procedures and make recommendations to each other to improve them.
- Continue to the next activities ...
Check on students daily and ask how they are meeting their goals. - Ask. How it is going? What went well? What didn't? and ask who has suggestions to help each other achieve their goals.
- At the end of each week have students summarize what they learned about goal setting and make suggestions on how setting and achieving goals can be successful.
Activity 2 - What's your character's mental health?
Materials:
- Character's mental health lab notes worksheet
- Five categories of mental health
- Sample Amy Cahill from 39 Clues, Book One: The Maze of Bones. by Rick Riordan.
- Sample Dan Cahill from 39 Clues, Book One: The Maze of Bones. by Rick Riordan.
Focus questions:
- What is it people do that suggests their mental / emotional health?
- How would you determine a person's mental / emotional health?
- What do people need to be able to do to have and maintain mental / emotional health?
- What state of mind do people need to have to set and achieve personal goals that maintain their health and wellness and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of focus question 1&2.
- Define mental/ emotional health and identify five categories of characteristics of a persons state of mind or suggest a person's mental / emotional health.
- Have students identify a character from a book, movie, TV show, or other media.
- Review examples of an analysis of the characters of Amy & Dan Cahill state of mind or mental / emotional health.
- Students analyze their selected characters state of mind or mental emotional health and share with the class.
Scoring guide for a character's mental health
Top level
- Selects a character, identifies media reference (book, video, ...), describes multiple characteristics for each of the five categories: belonging, purpose, outlook, self-esteem, and self-sufficient.
- Selects a character, identifies media reference (book, video, ...), describes multiple characteristics for three or four of the categories and one for the other one or two categories: belonging, purpose, outlook, self-esteem, and self-sufficient.
- Selects a character, identifies media reference (book, video, ...), describes at least one characteristic for each of the five categories: belonging, purpose, outlook, self-esteem, and self-sufficient.
Lower level
Exploration
Activity: What is mental / emotional health?
- Put students in groups.
- Ask. What is it people do that suggests their mental health? Accept all answers and if possible work toward ... everything they do, their behaviors, actions, procedures they use, goals they set, and how they do and don't achieve them.
- Ask. How would you determine a person's mental / emotional health? Accept all answers ...
Invention
Activity: Discuss mental health characteristics and identify examples
- Summarize the discussion of the first two focus questions.
- Mental health is determined from what people do, their thoughts, their behaviors, actions, procedures they use, goals they set, and how they do and don't achieve them.
- A person's mental health should be determined based on a definition of mental health.
Mental / emotional health is a state of emotional / mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals: that cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Ask. What do people need to be able to do to have and maintain good mental / emotional health? They need to set and achieve personal goals that maintain their health and wellness and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Say. To do this it is helpful to have a positive state of mind (state of mind is a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world that affects the choices they make and their behaviors, (mood)).
- Give students the data sheet: Five categories of mental / emotional health.
- Tell them they are going to go over the categories to get ideas be use to analyze people or characters behaviors to create a character's mental health profile. Like an author or detective might do.
- Tell them they can highlight or add notes to their mental / emotional health fact sheet.
DON'T WORRY ABOUT COMPREHENSIVENESS HERE AS THESE WILL BE REVISITED THREE MORE TIMES, in activity 4, 5, & 7. - Ask. What contributes to a positive state of mind, for people to be able to set and achieve personal goals, that maintain their health and wellness and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way? Have a sense of belonging, sense of purpose, be positive, believe in their ability to accomplish their goals (self-efficacy), and healthy self-esteem.
- Ask. How does each category relate to a person's state of mind?
- Belonging - provides connections to help and support each other achieve our needs Maslow's Hierarchy ...
- Sense of purpose - provides a reason for setting goals in ways to help us survive and create a better world.
- Be positive - to be happy and enjoy each other and to help other people be happy and successful.
- Believe in their ability to accomplish their goals (self-efficacy) - enables us to try to set and implement goals because we believe we know how to be successful to achieve our purposes.
- Healthy self-esteem - value yourself enough to set and achieve positive healthy actions.
- Ask. What you might observe people think, say, and do that relates to each of the five categories of mental health.
- Ask. What do people do to show they - belong or not?
- Are comfortable communicating with family members, peers, friends, teachers, and others ...
- Are social or unsocial. Care ... Saying hello to people, talking to them about the weather, ask how they are, what they are doing, what they are reading, watching, sports, ...
- Respect and advocate for self and others. Say good or bad things about people. Complement, stand-up, praise, put-down, criticize ...
- Communicate well with others. Easy to talk to, avoid confrontations, look the other way, don't look people in the eye.
- Stand up for self and others. Go along with what others say. Afraid to speak up for fear of not being accepted.
- Good social skills. easy to talk to other people. Make other people feel comfortable to be around. Appear not to know what to say or do with other people.
- Ask. What do people do to show they have a - sense of purpose or not?
- Different people have - have purposes you value and desire and are able to set and achieve goals in pursuit of those purposes.
- Meaning and purpose for life. Like being around other people. Want to help other people. Want to have fun. Want to play video games. Want to drink and party.
- Set and achieve goals. Take the initiative to do different activities. Have a life plan. Sit around waiting for someone to tell them what to do or ask them if they want to do something.
- Use refusal skills when presented with alternate goals counter to your personal goals. Independent to refuse invitations that don't fit with their personal goals. Will participate in any activity others suggest.
- Ask. What do people do to show they have a - Positive outlook or not?
- Optimistic, see the good and believe success is achievable.
- Being positive or being negative.
- Have happy and positive feelings
- Look for the good. Were always saying negative and bad things about people.
- Paying it forward.
- Doing a random acts of kindness
- Ask. What do people do to show they are - Self-sufficient or self-efficacy?
- Believe you are capable and able to achieve success.
- Competence - having the ability and skill to achieve success
- Critical thinking and make good decisions
- Use self-talk to motivate and achieve
- Take care of yourself - sleep, eat healthy with good nutrition, exercise, water, personal hygiene, bath, dental care, hair care.
- Avoid high risk behaviors
- Maintain appropriate weight
- Manage conflict
- Use Refusal skills
- Manage stress - procedures to manage stress
- Maintain self-control and avoid anger and resolve conflict, saying no, right of being assertive, manage anger,
- Relaxation techniques
- Health & dental check-ups
- Moderate use of caffeine caffeine and hormones
- Don't use tobacco, illegal drugs & use prescription drugs responsibly
- Ask. What do people do to show they have - Healthy self-esteem?
- You value, respect, and feel confident about yourself.
- May include ideas from #4...
- Self-esteem - how much you value, respect, and feel confident about yourself.
Discovery
Activity: Analyze mental health of a fictional character
- Ask students to identify one of their favorite characters from a book, movie, TV show, video, graphic novel, comic book, or other media and create a list on the board so all can see.
- Arrange students into groups. Put students into groups by the characters they selected. Try to keep group sizes between 2-4. I prefer multiple groups for the same character rather than a larger group for the same character. Also if there are students who were the only one who selected a character, would create a group with members who have different characters.
- Provide students with a Character's mental health lab notes worksheet.
- Tell students to use their Five categories of mental / emotional health fact sheet with notes and reference information for their character: books, reviews, videos, Wikipedia, or other media to describe the character's mental emotion health by listing examples of the characters behaviors in each of the five categories of mental health. Then, summarize by describing how the characteristics combine for the character's good and not so good mental health.
- It may be helpful to share these examples for the characters: Amy Cahill & Dan Cahill from 39 Clues, Book One: The Maze of Bones. by Rick Riordan to demonstrate how to complete the lab note sheet.
- Give groups of students time to research, complete their lab note sheet, and prepare to share with the class.
- Each group shares their analysis of their character's mental health with the class.
Activity 3 - What is human?
Materials:
- What is human lab notes
- Characteristics of humans fact sheet
- May want to share a video
- Self-Consciousness See Source: Dolphins in the mirror (5:03)
- Elephants have self-awareness, solve problems, and cooperate ... Source: Through the Worm hole (5:50)
- Dolphins cooperate with fishermen to catch fish. Source (3:41)
Focus questions:
- What is human?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Share a video...?
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their initial understanding of the focus question.
- Share list of human characteristics with students.
- Revise definition of what is human by listing human abilities.
Scoring guide for What is human?
Top level
- Describe what makes us human with five or more key attributes: communicate across time and distance, use , create fiction, teach their young, anticipate the future, fear, manipulate, walk upright with hands free to grasp, ...
- Describe what makes us human with one or two key attributes.
- Describe what makes us human with a generic definition that doesn't include attributes of what is human. Example: humans belong to the class of animals homo sapien.
Lower level
Exploration
What is human?
- Put students in groups.
- Tell. Human life is different than animals.
- Ask. What makes us human?
- Distribute. What is human lab notes.
- Let students brainstorm for about eight minutes on what is human.
- Share the information students have with the class.
Invention
Human characteristics
- Distribute the Characteristics of humans fact sheet.
- Review the information students brainstormed and compare it to information on the fact sheet.
- Let students edit it their description of what is human in their lab notes.
Activity 4 - Who am I?
Materials:
Focus questions:
- Who am I?
- How do I describe who and what I am?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Have students write their thoughts about the focus questions 1 & 2.
- Review ideas for coat of arms or shield
- Students create their coat of arms.
Scoring guide for Who am I? activity
Top level
- Included personal ideas for each of the five categories of emotional health and examples in lab notes. Some of which are reflected in their completed personal shield or coat of arms, which has at least five different ideas that represent them which they explained why three of them are important to them in their class presentation.
Lower level
Exploration
Who am I?
- Distribute the Who am I lab notes
- Have students answer the two focus questions in their lab notes.
- Who am I?
- How do I describe who and what I am?
Invention
Personal shield or coat of arms
- Tell students. Like characters in a book a person has characteristics that describe them.
- Ask. What characteristics do you want people to know you for?
- Tell. Your state of mind and mental / emotional health has a strong influence or impact on how a person acts and is known by other people. It is good for people to reflect on what they believe is important and describe it so they can set goals to become who they want to be and how others view them.
- Tell. One way to describe who you are is to first, brainstorm characteristics of what you value and what you want people to know about you.
- Tell. Write your ideas in your lab notes as they think of them.
- After students have a few ideas, have them use the categories of emotional health and their examples from previous activities to see if there are other ideas they want to include.
REMEMBER THESE IDEAS WILL BE USED TWO MORE TIMES, activity 5 & 7.- Belong - what social groups known to be associated with? family, school, band, team, gamer, reader, artist, musician, religion,
- Purpose - be creative, contribute, he helpful, friendly, physically fit, athlete, scholar, artist, musician, mechanic, construction, banker,
- Optimistic
- Self-efficacy - resilient, problem solver, helpful,
- Self-esteem - respect for self, honor, confident
- Give students time to record about five solid ideas.
- Tell. Use the information you have to include the ideas you value most to make messages for their coat of arms or shield that will powerfully represent them.
- For example what shapes best fit the ideas?
- What shapes, placements, use of color best fits the state of mind, life goals, personality, ... you want to communicate?
- The most important ideas or name in prominent positions?
- What best fits in different places?
- most important at the top - highest, or
- bottom - foundational ideas,
- center - as core ...
- What do different colors meant? Share the significance of different colors page.
- How many core ideas? and a section for each or some grouped together?
- Research traditional symbols used as heraldry messages. Click on the links for more specific examples ... Site isn't user friendly, but the information is comprehensive.
- The most important ideas or name in prominent positions?
- Tell. If you need more ideas, use the hints on the lab notes to generate them.
- One idea that describes you. Include a word, a symbol, or a picture that represents that idea in a panel of the shield. A historically example included on many coat of arms is - a lion for braver or king like.
- Something you like or like to do. Include symbols or pictures for each activity. Consider activities to include: physical, mental, and social activities.
- Something you are working at to become better. Write it or put a symbol to represent it in a panel.
- A symbol to represent a social or political cause you have believed in or would advocate for in your lifetime.
- Select words you would like people to use to describe you, and write or symbolize them in one panel of the shield.
- Examples: trustworthy, loyal, helpful, friendly, courteous, kind, cheerful, caring, fair, responsible, respectful, and a good citizen.
- Identify a major fantasy of what you yearn to do or would do if you had no restrictions. Draw a picture or note to represent it.
- Something to represent what has or could cause a positive big change in your way of living.
- Draw or symbolize the most important person in your life.
- Anything else you believe is important or want to be known as or for.
- Let students create their coat of arms or shield.
- Have students share their shield or coat or arms and identify at least three ideas they think are important to them.
Activity 5 - Effects on mental health, risks and promoting health and wellness
Materials:
- Effects on mental health, risks and promoting health and wellness Lab notes
- Categories of emotional mental health with examples fact sheet
Focus questions:
- What ideas and behaviors are indicators for states of mind that affect mental and emotional health and wellness?
- What does a person need to be able to do to have a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Ask the focus question
- Put students in groups
- Have students write indicators for each of the five areas of mental / emotional health in their lab notes.
- Share students indicators and add more as necessary.
- Ask. What does a person need to be able to do to have a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health?
- Review five things a person needs to do for a positive state of mind and mental health.
Scoring guide for
Top level
- Make an honest attempt to include ideas in each area. Don't worry about comprehensiveness as students will use ideas from this for the goal setting in activity 8.
- Don't complete the lab notes page.
Lower level
Exploration
What effects are there on mental / emotional health & wellness?
- Review with students the four categories of effects on health in the Health dimensions unit: 1. people (self and others), 2. genetics, 3. environment, and 4. media and technology do affect mental and emotional health.
- Ask. In what ways can these effects be used to identify ideas that can be used as indicators for a person's states of mind. Indicators to suggest mental and emotional health and wellness? Accept all answers.
- Move to invention.
Invention
- Put students in groups and provide the Effects on health, risks and promoting health and wellness Lab notes.
- Tell. Use the information from the previous activities (2 & 4) and any other information they have learned to identify indicators for states of mind that affect mental and emotional health and wellness and write their ideas in the categories below.
- State of mind is a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world that affects the choices they make and their behaviors.
- Mental and emotional health - is a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. To be able to cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Share their ideas and let them add ideas to their lab notes.
- Share student's ideas and let them add ideas to their mental health lab notes.
- Sense of belonging - Like to talk to others, manage emotions, like to talk about what they are doing, talk about others, join groups easily, are known to help others, hang out with others, belong to different groups, isolate from others, sit by their self at lunch, don't join groups, want to travel and meet new people, want to help others, believe all people are good and are worth helping
- Sense of purpose and achieve success - Set goals, achieve goals, don't achieve goals, help others, participate in activities ... reading, sports, listen to music, watch ... don't try, fail, avoid situations that require effort to achieve.
- Positive outlook - Manage emotions, cope with loss and grief, deal with anxiety and depression, like new situations, think they can achieve their goals, believe others can also achieve, put people down and focus on other people' negatives so they are among other negative people.
- Self-efficacy - like a challenge, avoid challenges, want to try new things, want to travel, believe they can be successful if they want to be ...
- Healthy self-esteem - I value, respect, and feel confident about my ability to ... don't value them self and others.
- Other - unconscious - people, genetics, environment, media & technology ... ; memories, nutrition, ...
- Ask. What does a person needs to be able to do to achieve a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health?
- Discuss and have them write ideas in their lab notes.
- Review ideas they have included and share the following five ideas:
- Need to know how to have their needs met. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
- Know how to set and achieve goals
- Develop good relationships and learn social skills to get along with people better. next Unit on Healthy Social Relationships
- Need to manage emotions:
- Recognize feelings
- Manage Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
- Manage fear,
- Manage guilt,
- Manage anger,
- Refusal skill,
- Cope with loss and grief,
- Deal with anxiety and depression
- Suicide prevention.
- Other - know your body (anatomy), nutrition, medicine & drugs, environmental health, physical fitness ...
- Tell students they will select from some of these ideas for a mental health investigation after you present information on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and ideas about stress and stress management.
Activity - 6 Investigate Maslow's Hierarchy, Stress, and Procedures to manage mental emotional health and wellness
Materials:
- Mental Health Information Lab Notes
- Lab notes for Management presentation
- Maslow's Hierarchy
- Sample investigation for stress
- Stress
- Procedures to Manage Emotions:
- How to Increase Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
- Recognize your feelings as emotionally related & defense mechanisms
- Procedure to Manage Fear
- Procedure to Manage Guilt
- Procedure to Manage Anger
- Procedure to Manage and Deal with Stressful Situations
- Coping with loss and grief: Five Stages of grief or loss
- Dealing with Anxiety and Depression
- Suicide Prevention and Getting Help
Focus questions:
- What do people need to know to manage emotional / mental health?
- How is a person's state of mind important?
- What do people need to do to have good mental health and wellness?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Review five things people need to know to manage mental and emotional health.
- Talk about the importance of state of mind.
- Introduce Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
- Introduce stress and stress management
- Assign investigation topics, investigate, and share.
Scoring guide that is activity specific
Top level
- Define what they are investigating (see word bank), its feelings and possible causes, acceptable procedure to manage or prevent it, and a believable script to demonstrate management or prevention.
- Define what they are investigating (see word bank), its feelings and possible causes, questionable procedure to manage or prevent it, and a questionable script to demonstrate management or prevention.
- Define what they are investigating (see word bank), its feelings and possible causes, partial procedure to manage or prevent it, and a partial script to demonstrate management or prevention.
- Define what they are investigating (see word bank), some possible and not probable feelings and missing a cause, procedure is more a list of ideas rather than a sequence to manage or prevent it, and the script didn't demonstrate how to manage or prevent.
Lower level
Scoring guide to use for developing health literacy
Health literacy scoring guide based on national health standards
Exploration
- Ask. What do people need to know to manage emotional / mental health?
- They need to know how to have their needs met.
- Know how to set and achieve goals
- How to develop good relationships with people.
- How to manage emotions
- Other - Know your body (anatomy), nutrition, medicine & drugs, environmental health, physical fitness ...
- Ask. How is a person's state of mind important? A person's State of mind is the mood that influences their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world and that affects the choices they make and their behaviors. A good state of mind will make better choices than a negative state of mind.
- What do people need to do to have good mental health and wellness? They need to have their needs met as they set and achieve their personal goals. To have a state of mind that enables them to cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Tell them you are going to look at a chart that describes human needs and then together you will work on a writing procedures for positive mental health.
Invention
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs:
- Display Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and explain how it is a good example of the needs people have and how they are important to be met so people are able to feel they belong, can achieve a positive state of mind, have self-efficacy to achieve their goals and have purpose of life.
- Have students write in their lab notes: How people can use Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs to promote mental health? To know what needs people require before they feel they belong, can achieve a positive state of mind, have self-efficacy to achieve their goals and have purpose of life. .
How to recognize and develop procedures to manage emotions:
- Tell. I am going to demonstrate how you are going to do an investigate to manage an emotion. I will be doing stress. See Sample investigation for stress in lesson plan.
- Give a copy of lab notes Lab notes for Management presentation
- Have students fill in Topic - Stress
- Ask. What is stress. Suggest to look in word bank.
- Hav students fill in - Stress is the reaction of the body and mind to everyday opportunities, challenges, and demands.
- Tell. The first thing a stressed person has to do is to recognize their feelings are caused by stress. So..
- Ask. How do we identify stressful feelings?
Stress:
- Have students look at the procedure: recognize your feelings on the Procedures to Manage Emotions fact sheet
- Ask. What might you feel like if you were stressed? nervous, worried, anxious, tired,
- Have students fill in. Procedure and script for dealing with stress.
- Tell. So the first thing to put in the procedure and self-talk script is ... Recognize an emotional feeling.
- Work with students to develop a procedure similar to...
- Recognize an emotional feeling. I am feeling emotional. I feel ... Insert student's answers from their response to what they feel when stressed: nervous, worried, anxious ... I think it is stress related.
- Ask. Why you might feel this way? Because I have a concert, presentation, game, trip ...
- Ask. Is this event really important? Yes. I really want / need to do this.
- Should I wait? No. This is a one time deal and I need to do it.
- What can I do to feel better? Who or what might help? Research ...
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism? No I thought about denying or repressing the feeling, but decided it was stress related and will do something..
- Tell students all of their procedures and scripts will start the same way However, they only need to include defense mechanisms they think are appropriate.
Procedure and script for dealing with stress.
Stress information activities
- Tell students you will come back to finish the procedure and script after you review the fact sheets with research information for stress.
- Display stress fact sheets or provide students with them for a walk through research session.
- Tell. Look at the list of teen stressors.
- Ask. Do you believe these cause stress? OK.
- Say. So ideas for the procedure and script for stress can be checked with ideas on this list.
- Do the ideas I included: nervous, worried, anxious, concert, presentation, game, trip appear on the teen stressors list? Yes.
- Where? Second polka-dot under school.
- What other ideas might you choose in place of the ones in the example? Accept all reasonable suggestions
- Tell. Look at the Bodily responses to alarm, stress, and chronic stress This fact sheet has responses and feelings that can be used to help identify a stressful emotional feeling as well as body changes.
- Are the feelings we included in the list? Yes
- Which ones? Fear, anxiety is ... not worry, nervous ...
- Are there other ones that should also be included? Could add increase heart rate, sweating, desire to avoid or run away (flight), digestion problems, ...
- Tell. Look at Ways to manage and reduce stress,
- Tell. Return to their lab notes and work with them to write procedure to manage stress. See Sample investigation for stress for ideas
- Tell. Think of a situation when you were stressed.
- Tell. Pretend you were using the procedure for that situation and write what you would do as a script for the situation. see Sample investigation for stress
Sample presentation, procedure, and script notes to manage emotions
Topic Stress
Definition or description of topic
Stress is the reaction of the body and mind to everyday opportunities, challenges, and demands.
Describe feelings and recognize as an emotion
nervous, worried, anxious, tired, ... Stress
How do people manage
- Ask why might I feel this way?
- Is this really important for my well being or future?
- Should I wait before responding?
- What could I do to feel better?
- Who might I talk to to feel better or get help?
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism?
Defense mechanisms
- Compensation, make up for mistake or weakness by hard work, giving a gift, or other measures. Over compensation is taking compensation to extremes. Paying double or triple the price.
- Denial, don't recognize something that is obvious to others.
- Projection, attribute or blame your feelings, faults, or mistakes to others.
- Rationalization, create excuses to explain a behavior or situation rather than take responsibility.
- Regression, use a behavior that is recognized as immature rather than dealing with a situation in a more appropriate manner.
- Repression, deny the existence of unpleasant feelings or situation by ignoring it and putting it out of mind.
Procedure to manage
- Recognize an emotional feeling. I am feeling emotional. I feel nervous, worried, anxious ... I think it is stress related.
- Ask. Why you might feel this way? Because I have a concert, presentation, game, trip ...
- Ask. Is this event really important? Yes. I really want / need to do this.
- Should I wait? No. This is a one time deal and I need to do it.
- What can I do to feel better? Who or what might help? Research ...
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism? No I am not going to deny my feelings or repress them. I am going to take charge.
- Take charge. Tell my self I will survive and I am ready and will accept and enjoy whatever happens.
- Use self-talk to implement plan and review what you will do when you have thoughts about the up coming event.
- Manage time to review or practice, eat (diet), rest, and sleep.
- Review a planned relaxation technique and use when feel it would help.
Script (remember to use self talk)
- I am feeling wiggly, nervous, worried, or anxious
- I think it is stress related.
- Wonder if it is about the concert, presentation, game, trip ...
- Probably.
- It is really important and I really want / need to do this.
- I am not going to deny my feelings or repress them.
- I am going to take charge and change them.
- Think ...
- I will survive.
- I am ready and will enjoy whatever happens.
- Initiate relaxation technique appropriate for where I am.
- Wiggle, breathe, stretch, and say or think ...
- I accept it.
I love and accept myself.
I am calming and relaxing
The anxiety in my body is leaving and it feels calmer as I control it.
Tell students they will select and investigate ways to manage emotions and complete lab notes for it to present to the class.
Discovery
Activity - Investigate ways to manage emotions and write a procedure and script
Suggested ORGANIZATION:
- Let students select or assign groups to investigate ways to manage emotions from the list and make a procedure to manage it and write a script to demonstrate its implementation and present both to the class.
- Manage Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
- Manage fear,
- Manage guilt,
- Manage anger,
- Refusal skill, or how to deal with avoiding something that isn't beneficial or do not what to participate in.
- Cope with loss and grief,
- Deal with anxiety and depression
- Suicide prevention
- Give students Lab notes for Management Emotions presentation ...
- Work in groups
- Present
Activity - 7 Crossword puzzles
Materials:
Focus questions:
- How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Ask. How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
- Share word list and crossword puzzles in lab notes.
- Let students work in groups to solve the puzzles.
Scoring guide for crossword puzzles
Top level
- 100% complete and correct
- 100% complete and 90% or more correct
- 90% complete and 80% or more correct
- Less than 80% complete
Lower level
Exploration
- Ask. How well do you know vocabulary of mental and emotional health?
- You can work in groups to review the vocabulary in the word bank and to complete the crossword puzzles.
Invention
Have students share their experiences about the vocabulary and what they learned doing the puzzles.
Activity - 8 Create a mental health action plan
Materials:
Focus questions:
- What ideas do I have for my mental / emotional health?
Suggested procedures overview:
- Tell students they are goal to use what they learned about goal setting to write goals for mental health and identify procedures manage their mental health.
Scoring guide for
Top level
- Use a goal setting process to write a plan to implement them to maintain mental health. Include: a healthy person must know 1. their needs and how to meet them, 2. ability to manage emotions, 3. knowing how to set goals and achieved them to maintain health, 4. good health requires healthy social relationships, and 5. accurate knowledge to make good decisions necessary for health and wellness. Includes a plan with suggestions of procedures to implement and monitor.
- Identifies a ideas for health that mentions multiple factors for good health that include: meet needs, set goals, social relationships, manage emotions and accurate information. List some steps to manage emotions and monitor healthy with accurate information.
- Identify general ideas and list some steps for different ways to manage emotions.
- Has a statement as a plan and lists statements to manage emotions.
Lower level
Exploration
- Ask. What ideas do you have for your mental / emotional health?
- Tell. You can get ideas from what you have on your shield or coat of arms or from other lab notes you have.
- Accept all ideas and move to Invention.
Invention
- Give students the Lab notes to create a mental health action plan
- Review:
- Health, is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
- Health literacy is the ability of a person or group to understand and use information and services for one's health and wellness.
- Health skills are ideas and strategies used to deal with everyday life demands and challenges to maintain health and wellness. See Health Introduction word bank for list of some health skills.
- Review five things a person needs to be able to do to manage emotional and mental health to achieve a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health.
- Know how to set and achieve goals
- They need to know how to have their needs met.
- How to manage emotions
- How to develop good relationships with people.
- Other - Know your body (anatomy), nutrition, medicine & drugs, environmental health, physical fitness ...
- The four Steps to set and achieve goals
- Focus
- Select a goal
- Select effective strategies.
- Monitor, evaluate, and reflect
- Tell. A good way to Focus, is to page through their lab notes and pull out ideas for each topic they might use in a plan for good mental health and write them on the lab note page.
- Next pull out ideas and write your action plan for mental health.
- Decide how much detail you will expect from students and what kind of guidance or support they will need. The Lab notes include a writing prompt, but the notes below have teaching plans without a prompt and with a prompt.
Teaching notes for students writing: without a prompt and with a prompt:
Without a prompt.
- Let students write for awhile and then share.
- Tell. Review your action plan for mental health to see if it is comprehensive.
- Does it include the five ideas people need to know for mental / emotional health? 1. How to set and achieve Goals 2. Needs that must be met 3. how Emotions are managed and 4. how good relationships with people (social) and 5. Knowledge is necessary. AND include procedures to achieve and monitor them.
- A possible starter:
- By knowing myself and understanding my body, how it works, and its needs, I can work with others to make good choices, set goals, decide on procedures to implement and monitor progress to achieve mental health. I recognize my physical needs: sleep, water, food, and safety need to be met before my emotional ones (belonging, love, self-actualization and emotional success). I will achieve mental health when I feel I (belong, have purpose, a positive outlook, have self-efficacy, and self-esteem. I will monitor and manage my feelings as I go through every day life by ... .
- I will make adjustments to maintain my self-identity (coat of arms or personal shield ideas)
- I will manage my self-esteem, fear, guilt, anger, stress, refusal skills, loss, grief, ... ) by ...
With a writing prompt:
- Review the writing prompt on the lab notes and answer student questions.
- Let then begin writing.
- Writing Prompt:
- By knowing myself and understanding how my body works I can work with others to make good choices, set goals: ... (fact sheet) to ...
I recognize my basic needs of ... (fact sheet) - Must be met before my emotional ones of ... (fact sheet)
- can be met.
- I will achieve my mental health of ... (fact sheet)
- by monitoring and managing my feelings as I go through every day life by ... . (fact sheet)
- I will make adjustments to maintain my self-identity of ... (Who am I lab notes)
- I will manage my (self-esteem, fear, guilt, anger, stress, refusal skills, loss, grief, ... ) by ... (fact sheets)
Activity 9 - Review
Materials:
- Activity 9 - Review - External page
- Review answer key - External page
Focus questions:
- How much do you remember from this unit?
Learning outcomes:
- Write responses that review learning outcomes for this unit.
Suggested procedures overview:
- Put students in groups, focus their attention, and assess their understanding with the review.
- Discuss students answers and let them improve their responses as necessary.
Exploration
- Put students in pairs or small groups.
- Ask. How much do you remember from this unit?
- I have a review to challenge you.
- Distribute the Review
- Let students complete the review.
Invention
- Review student answers and help them edit their responses to make them more accurate. Use key as necessary.
Lab Notes for activities
My goal setting notes (1)
Focus
Goal
Procedure and Strategies
How to monitor, evaluate, and reflect on the goal, plan, and implementation
Week one
- Day 1
- Day 2
- Day 3
- Day 4
- Day 5
- Day 6
- Day 7
Summary for week one
Week two
- Day 1
- Day 2
- Day 3
- Day 4
- Day 5
- Day 6
- Day 7
Summary for week two
What's your Character's Mental Health? (2)
Determine the mental health of a character in a book or other media source.
Select a character from a media source: movie, TV, video, graphic novel, comic book, or other. Use information about the character and describe the character's mental emotion health for each of the five characteristics. Summarize by describing how the characteristics combine for the character's good and not so good mental health.
For suggestions see the Categories of mental and emotional health and examples fact sheet. For a finished sample see an analysis of the mental and emotional health of the characters: Amy Cahill & Dan Cahill from 39 Clues, Book One: The Maze of Bones. by Rick Riordan.

Summary
What is Human? (3)
Human life is different than animals.
Use the information about what you believe make people human and information on the Fact sheet: What is human? and any other information you desire to answer the question.
What makes us human?
Who Am I? (4)
Who am I?
How do I describe who and what I am?
Review the five categories of emotional health indicators and their examples and briefly list ideas you might want to include for each category.
1. Belong -
2. Purpose -
3. Positive -
4. Self-efficacy -
5. Self-esteem -
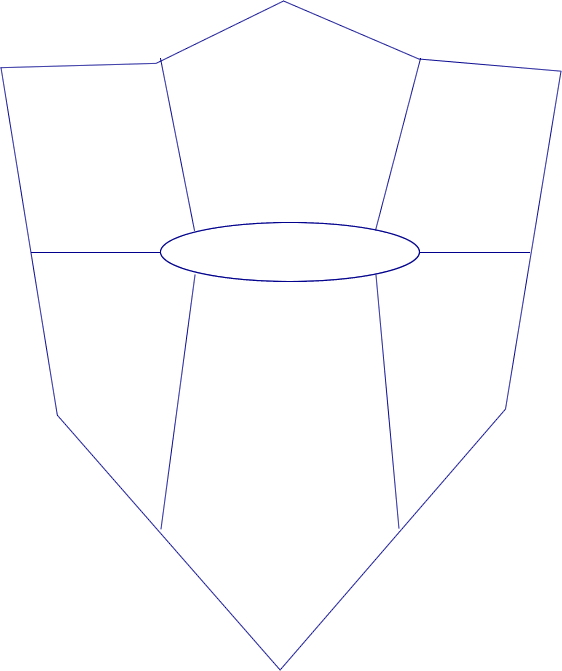
One way to describe who you are is to create a personal shield or coat of arms. Below is a procedure to create a Personal Shield or Coat of Arms.
Personal Shield or Coat of Arms
- Select a shape, or make one one on paper or with a sketch program. Or use the following shape.
- Suggestions about shape, placement, use of color:
- A title, which is usually your name is placed in a prominent position, oval.
- Decide where to put the ideas that describe you in each section of your shield. Consider the significance of each to help determine their placement. Top could be most important, bottom foundational ideas, center as core ...
- Different colors have different meanings for different people. Consider the use of color and the significance of different colors.
- The following shield was designed for six core ideas, but may be altered to include additional.
- There are symbols that have been traditional used as heraldry symbols. You may want to research some of these meanings.
- A title, which is usually your name is placed in a prominent position, oval.
- Use the ideas from the following list to consider words, phrases, and pictures to use to describe you.
Hints. Or ideas to consider to represent you.
- One idea that describes you. Include a word, a symbol, or a picture that represents that idea in a panel of the shield. A historically example included on may coat or arms is a lion for braver or king like.
- Something you like or like to do. Include symbols or pictures for each activity. Consider activities to include: physical, mental, and social activities.
- Something you are working at to become better. Write it or put a symbol to represent it in a panel.
- A symbol to represent a social or political cause you have believed in or would advocate for in your lifetime.
- Select words you would like people to use to describe you, and write or symbolize them in one panel of the shield. Examples: trustworthy, loyal, helpful, friendly, courteous, kind, cheerful, caring, fair, responsible, respectful, and a good citizen.
- Identify a major fantasy of what you yearn to do or would do if you had no restrictions. Draw a picture or note to represent it.
- Something to represent what has or could cause a positive big change in your way of living.
- Draw or symbolize the most important person in your life.
- Anything else you believe is important or want to be known as or for.
Pattern on next page
Effects on mental health, risks and promoting health and wellness (5)
Use the information from the activity - Who am I? and other information you have learned to identify indicators for states of mind that affect mental and emotional health and wellness. Write your ideas in the categories below.
State of mind is a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world that affects the choices they make and their behaviors.
Mental and emotional health - is a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. To be able to cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
- Sense of belonging - comfortable communicating with family members, peers, friends, teachers, and others who support you.
- Sense of purpose - have things you value and desire and are able to set and achieve goals in pursuit of that purpose.
- Positive outlook - See the good and believe success is achievable.
- Self-efficacy - believe you are capable and able to achieve success.
- Healthy self-esteem - you value, respect, and feel confident about yourself.
- Other.
What are five things a person needs to be able to do to achieve a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Mental and emotional information to promote wellness notes (6)
How can people use Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs to promote mental health?
How do people manage their emotions?
How do people recognize feelings?
How do people manage Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity?
How do people manage fear?
How do people manage guilt?
How do people manage anger?
How do people cope with loss and grief?
How do people deal with anxiety and depression?
How do people manage stress?
Health management presentation, procedure, and script notes (6)
Topic
Definition or description of topic
Describe feelings and recognize as an emotion
How do people manage
- Ask why might I feel this way?
- Is this really important for my well being or future?
- Should I wait before responding?
- What could I do to feel better?
- Who might I talk to to feel better or get help?
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism?
Defense mechanisms
- Compensation, make up for mistake or weakness by hard work, giving a gift, or other measures. Over compensation is taking compensation to extremes. Paying double or triple the price.
- Denial, don't recognize something that is obvious to others.
- Projection, attribute or blame your feelings, faults, or mistakes to others.
- Rationalization, create excuses to explain a behavior or situation rather than take responsibility.
- Regression, use a behavior that is recognized as immature rather than dealing with a situation in a more appropriate manner.
- Repression, deny the existence of unpleasant feelings or situation by ignoring it and putting it out of mind.
Procedure to manage
Script (remember to use self talk)
Health management presentation, procedure, and script notes (6)
Topic
Definition or description of topic
Describe feelings and recognize as an emotion
How do people manage
- Ask why might I feel this way?
- Is this really important for my well being or future?
- Should I wait before responding?
- What could I do to feel better?
- Who might I talk to to feel better or get help?
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism?
Defense mechanisms
- Compensation, make up for mistake or weakness by hard work, giving a gift, or other measures. Over compensation is taking compensation to extremes. Paying double or triple the price.
- Denial, don't recognize something that is obvious to others.
- Projection, attribute or blame your feelings, faults, or mistakes to others.
- Rationalization, create excuses to explain a behavior or situation rather than take responsibility.
- Regression, use a behavior that is recognized as immature rather than dealing with a situation in a more appropriate manner.
- Repression, deny the existence of unpleasant feelings or situation by ignoring it and putting it out of mind.
Procedure to manage
Script (remember to use self talk)
Across
4. spending money to buy stuff that is not needed. (two words)
8. the combined qualities that describe how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
9. a mental state or prolonged feelings of helplessness, hopelessness, sadness, despair, apathy, and discouragement.
11. a feeling of the lose of hope, lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern.
12. a strong feeling of sorrow, misery, sadness, anguish, pain, heartache, heartbreak, agony, or torment over loss.
14. power within ourselves that is strongly affected from outside, social and physical objects.
17. the skill and ability to do something.
20. a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world. (three words)
23. a professional trained to give guidance on personal, social, or psychological problems.
24. chemicals produced by your glands that regulate bodily actions and cell behaviors.
26. dealing successfully with life changes.
27. ability to adapt and recover from disappointment, set-backs, crisis, or other goal blocking situations.
28. the reaction of the body and mind to everyday opportunities, challenges, and demands.
30. a feeling of unease, stress, or worry about what might happen.
Down
1. the way a person acts.
2. an irrational fear of something specific such as snakes, height, or social occasions.
3. sticking to core ethical values.
5. the ability to imagine and understand how someone else feels.
6. things necessary for survival and health.
7. an unpleasant feeling caused by an emotional reaction to a belief that someone or something is dangerous and could cause pain, a threat, serious injury or death.
10. the process of becoming aware of information with your senses (eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue)
11. a strong feeling of annoyance, displeasure, rage, fury, or hostility
13. signals that effect how you feel and can consciously and unconsciously cause body reactions and behaviors.
15. a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. (two words)
16. a complex set of characteristics that make a person unique.
18. an emotional reaction of wrong doing or regret, imagined or real, for failing to be responsible or for committing an offense, crime, or wrong.
19. is a person's sense of them self as a unique individual. (two words)
21. a state of mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals, cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way. (two words)
22. the use of drugs to treat medical disorders. (two words)
25. the belief in your ability to learn, change, accomplish success or failure (hyphenated word)
29. the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself. (hyphenated word)
Across
2. a series of suicides that happen in a short period of time in the same geographical area. (two words)
4. unplanned stealing of stuff.
7. being able to achieve success (two words)
8. the decisions a person makes about the behaviors they choose that affects their health and wellness. (hypenated word)
10. when a person is persistently driven by anxiety or fear to repeat a behavior over and over. (three words)
13. can happen after experiencing a terrifying event (four words)
19. the intentional use of unfriendly or offensive behaviors.
23. most common mental disorder caused by real or imagined fears. (two words)
28. a professional who specializes in the study of emotional, mental, and social, aspects of school aged students and the effects they have on student learning and behavior. (two words)
29. indicated by continued elevated amounts of adrenaline and cortisol in the blood stream. (two words)
30. continual gambling with excessive losses. (two words)
31. the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself. (hypenated word)
32. a mark or feeling of shame or disapproval from being isolated, shunned, or rejected.
33. nervosa is a mental characterized by consumption of large amounts of food (binge) and ridding of the food (purge). (two words)
34. ideas, beliefs, and attitudes a person holds precious and use to guide their life.
35. a medical doctor who specializes in the mental disorders and can prescribe mediation.
36. the intentional taking of one's own life.
37. a sudden unexplained feeling of fear and terror. (two words)
38. the act of showing sorrow, regret, and grief when someone dies.
39. a sudden and shocking situation that overwhelms all normal coping strategies that provided confidence and security. (two words)
40. cutting the body for pleasure. (two words)
41. the stages a person may go through when they experience a loss. (three words)
Down
1. illness with emotional extremes that interfere with everyday life. (two words)
3. discussion and interventions with professionals intended to guide and help addicted individuals stop compulsive drug use. (three words)
5. treatment for behavioral problems with a focuses on changing
6. a mental and physical disorder characterized by loss of weight brought on by an unrealistic fears. (two words)
9. mental processes used to protect us from strong feelings and stressful emotions. (two words)
11. a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. (two words)
12. illnesses of the mind that affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of people and prevents them from leading happy, healthful, and productive lives. (two words)
13. a physical reaction that results from a mental factor such as mental conflict or stress not from a physical illness or injury. (two words)
14. a feeling of being isolated and separated from people.
15. the belief in your ability to learn, change, accomplish success or failure (hypenated word)
16. when family members meet with a professional to learn how to communicate better, understand each other, and seek solutions for problems in positive ways. (two words)
17. spending money to buy stuff that is not needed. (two words)
18. when a group of people with a similar situation or problem meet regularly with a professional therapist to discuss ways to cope and live happy and productive lives. (two words)
20. non-hostile comments that suggest a problem, assist in resolving it, and encourage positive change. (two words)
21. a doctor who specializes in the brain, nerves, and nervous system.
22. behavior interferes with the rights of others: stealing, lying, aggression, violence, truancy, arson, or vandalism. (two words)
24. is something that cause stress.
25. a state of mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals, cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way. (two words)
26. setting fires for pleasure.
27. the treatment of mental disorders with an ongoing discussion to find a cause and solution for a problem rather than by medical means alone.
31. a mental disorder where a person has delusions, hallucinations, or other loses of contact with reality.
Across
5. when a person is persistently driven by anxiety or fear to repeat a behavior over and over. (three words)
7. the treatment of mental disorders with an ongoing discussion to find a cause and solution for a problem rather than by medical means alone.
9. the decisions a person makes about the behaviors they choose that affects their health and wellness. (hyphenated word)
10. a state of mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals, cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way. (two words)
12. signals that effect how you feel and can consciously and unconsciously cause body reactions and behaviors.
14. a feeling of the lose of hope, lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern.
15. a mark or feeling of shame or disapproval from being isolated, shunned, or rejected.
16. ideas, beliefs, and attitudes a person holds precious and use to guide their life.
17. indicated by continued elevated amounts of adrenaline and cortisol in the blood stream. (two words)
18. ability to adapt and recover from disappointment, set-backs, crisis, or other goal blocking situations.
22. is a person's sense of them self as a unique individual. (two words)
23. is something that cause stress.
24. a person whose success and behavior is emulated. (two words)
29. a strong feeling of sorrow, misery, sadness, anguish, pain, heartache, heartbreak, agony, or torment over loss.
30. a physical reaction that results from a mental factor such as mental conflict or stress not from a physical illness or injury. (two words)
32. setting fires for pleasure.
33. dealing successfully with life changes.
35. unplanned stealing of stuff.
37. a doctor who specializes in the brain, nerves, and nervous system.
38. chemicals produced by your glands that regulate bodily actions and cell behaviors.
40. an emotional reaction of wrong doing or regret, imagined or real, for failing to be responsible or for committing an offense, crime, or wrong.
41. the reaction of the body and mind to everyday opportunities, challenges, and demands.
45. illness with emotional extremes that interfere with everyday life. (two words)
47. the combined qualities that describe how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
48. a sudden unexplained feeling of fear and terror. (two words)
49. a complex set of characteristics that make a person unique.
50. a feeling of being isolated and separated from people.
51. when a group of people with a similar situation or problem meet regularly with a professional therapist to discuss ways to cope and live happy and productive lives. (two words)
52. an irrational fear of something specific such as snakes, height, or social occasions.
53. the intentional use of unfriendly or offensive behaviors.
54. a sudden and shocking situation that overwhelms all normal coping strategies that provided confidence and security. (two words)
57. the stages a person may go through when they experience a loss. (three words)
60. a series of suicides that happen in a short period of time in the same geographical area. (two words)
61. continual gambling with excessive losses. (two words)
62. being able to achieve success (two words)
63. treatment for behavioral problems with a focuses on changing behavior with reinforcement (reward, punishment, time-out). (two words)
64. sticking to core ethical values.
Down
1. a professional trained to give guidance on personal, social, or psychological problems.
2. behavior interferes with the rights of others: stealing, lying, aggression, violence, truancy, arson, or vandalism. (two words)
3. a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. (two words)
4. spending money to buy stuff that is not needed. (two words)
6. mental processes used to protect us from strong feelings and stressful emotions. (two words)
7. the process of becoming aware of information with your senses (eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue)
8. a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world. (three words)
11. most common mental disorder caused by real or imagined fears. (two words)
13. illnesses of the mind that affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of people and prevents them from leading happy, healthful, and productive lives. (two words)
14. a mental and physical disorder characterized by loss of weight brought on by an unrealistic fears. (two words)
19. power within ourselves that is strongly affected from outside, social and physical objects.
20. a mental state or prolonged feelings of helplessness, hopelessness, sadness, despair, apathy, and discouragement.
21. cutting the body for pleasure. (two words)
25. nervosa is a mental characterized by consumption of large amounts of food (binge) and ridding of the food (purge). (two words)
26. a strong feeling of annoyance, displeasure, rage, fury, or hostility
27. a medical doctor who specializes in the mental disorders and can prescribe mediation.
28. the skill and ability to do something.
31. the intentional taking of one's own life.
34. things necessary for survival and health.
36. a mental disorder where a person has delusions, hallucinations, or other loses of contact with reality.
39. when family members meet with a professional to learn how to communicate better, understand each other, and seek solutions for problems in positive ways. (two words)
42. the belief in your ability to learn, change, accomplish success or failure (hyphenated word)
43. the use of drugs to treat medical disorders. (two words)
44. an unpleasant feeling caused by an emotional reaction to a belief that someone or something is dangerous and could cause pain, a threat, serious injury or death.
46. discussion and interventions with professionals intended to guide and help addicted individuals stop compulsive drug use. (three words)
55. the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself. (hyphenated word)
56. the act of showing sorrow, regret, and grief when someone dies.
58. the ability to imagine and understand how someone else feels.
59. a feeling of unease, stress, or worry about what might happen.
Create an action plan for healthy social and emotional life (8)
Review:
- Health, is a state of complete physical, emotional and social well-being.
- Health literacy is the ability of a person or group to understand and use information and services for one's health and wellness.
- Health skills are ideas and strategies used to deal with everyday life demands and challenges to maintain health and wellness. See Health Introduction word bank for list of some health skills.
- Review five things a person needs to be able to do to manage emotional and mental health to achieve a positive state of mind and exhibit mental health.
- Know how to set and achieve goals
- They need to know how to have their needs met.
- How to manage emotions
- How to develop good relationships with people
- Other - Know your body (anatomy), nutrition, medicine & drugs, environmental health, physical fitness ...
- The four Steps to set and achieve goals
- Focus
- Select a goal
- Select effective strategies.
- Monitor, evaluate, and reflect
Four step goal setting process to Set a goal for a positive state of mind and mental health
Focus
Use your lab notes and jot down ideas important to you for each category below. This will help focus your thinking on goals to help you better achieve a positive state of mind and mental health.
1. Goal related to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
2. Goal to set and achieve goals
3. Manage emotions
4. Manage Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
5. Manage fear
6. Manage guilt
7. Manage anger
8. Manage and reduce stress
9. Increase immunity
10. Cope with loss and grief
11. Deal with anxiety and depression.
Write your mental health action plan.
- Writing Prompt:
- By knowing myself and understanding how my body works I can work with others to make good choices, set goals: ... (fact sheet) to ...
I recognize my basic needs of ... (fact sheet) - Must be met before my emotional ones of ... (fact sheet)
- can be met.
- I will achieve my mental health of ... (fact sheet)
- by monitoring and managing my feelings as I go through every day life by ... . (fact sheet)
- I will make adjustments to maintain my self-identity of ... (Who am I lab notes)
- I will manage my (self-esteem, fear, guilt, anger, stress, refusal skills, loss, grief, ... ) by ... (fact sheets)
_____________________________ Mental health action plan
Fact Sheets
Setting and achieving goals
Four Step process
- Focus on getting started
- Select a goal
- Select a plan or process to achieve it and implement it.
- Monitor and adjust
Explanation and suggestions for setting and achieving goals
- Focus on the situation and recognize a need for change. Think of how it will help you, how it may help others, how you will feel after you accomplish it, and then the hardest part is just getting started. So go...
- Select a goal
- State the goal clearly. What will be done when it is achieved.
- I walk / jog 20 laps or twenty minutes each day.
- I will read a book of my choice at least 30 minutes each day.
- I will do 15 push-ups after each TV program I watch.
- Check to see if the goal is realistic and attainable.
- Have I done this before?
- Are you trying to do too much for two weeks. For example: If you can only do 15 push-ups now, then start with 16, instead of 30. Then increase by 1 each day so you can do 3o at the end.
- State the goal clearly. What will be done when it is achieved.
- Select effective strategies. Write a procedure for your plan to implement and achieve your goal.
- Write your procedure for achieving the goal. Include suggested time to start and how to record your progress.
- I will go to the rec center at __:___and walk and jog on the track 20 laps or for twenty minutes each day after school and on week ends in the early afternoon.
- I will choose a book and read for at least 30 minutes each evening. I will sit on a chair in a quiet place (living room, den, kitchen ...) from 8:00 - 8:30 each night.
- Write your procedure for achieving the goal. Include suggested time to start and how to record your progress.
- Monitor, evaluate, and reflect how to monitor the progress of the procedure to achieve the goal and how to adjust if necessary.
- I will record what I do each day, think about my achievement, and get psyched for tomorrow.
Characteristics of humans
- Walk upright (bipedal)
- Run for long distances
- Opposable thumbs
- Persistent curiosity, habits of mind
- Collaborate with family, friends, & strangers, across gender, animals, and other tribes or groups.
- Create see a point in the end of a stick, a scraper in a rock, and combine two objects to make one tool ...
- Process food: butcher animals, fillet fish, dry food, cook, smoke, salt, preserve
- Develop tools, technology, domestication of plants and animals
- Foresight - anticipate and see the future
- Fear the future
- Complex brain
- Logic
- Language and communicate across time and long distances, gossip, tell stories, art, music ...
- Social
- Read people's body expressions to anticipate their thinking one, two, three, four, or more steps into the future.
- Able to speculate on what other people are thinking and to speculate that they are capable of thinking about what I am thinking that they are thinking ... and so forth...
- Hate for our enemies
- Create ideas that are not real or have physical properties: art, music, fiction, speculation, lies, stories, myths, explanations, theories, ...
- Consciousness aware that we are curious, social, and have awareness of our selves and individuals.
- Have the capacity to intervene for ourselves and to change the world.
- One form of intervention is learning and teaching.
Animals characteristics compared
Elephants
- Seem to have self awareness, consciousness, if, then thinking to explore, and the ability to think about what other elephants are thinking and cooperation ... Source: Through the Worm hole (5:50)
- Elephants were brought to a giant mirror where they viewed the image and explored it until they seemed convinced it was their own image in real time, not a picture, or video, of them self or another elephant. Then they explored areas of their body they could not see with out the mirror, nose, mouth, ...
- Two elephants were shown an apparatus where they worked together to solve a problem. Cooperation for problem solving.
Dolphins
- Self-Consciousness See Source: Dolphins in the mirror (5:03)
- Dolphins cooperate to create a circle of mud that act as a wall or net around a shole of fish. When the circle is closed, the fish attempt to escape by jumping over the mud, where the dolphin catch them. Source (1:38) Circles were observed from space satellites off the coast of southern Florida. Source What on Earth? documentary
- Dolphins off the coast of Laguna, Brazil cooperate with fishermen by herding mullets (fish) towards the shoreline, then signal the fishermen the best time for the fishermen to cast their nets. Source (3:41)
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow was concerned with how people develop their identity and humanness. He believed people develop their identity as they have their needs met and those needs formed a hierarchy, from the lowest, basic physical needs to highest, self-actualization.
For example, a hungry child will not develop much intellectual curiosity. Lower level physical needs (hunger amount them) must be reasonably well satisfied before any individual will attend to higher levels (intellectual curiosity being among the self-actualization).
Hierarchy of Needs Levels from lower to higher:
- Physical needs,
- Safety needs,
- Belonging & love,
- Esteem and feeling of being recognized, and
- Striving for self-actualization or to reach one's best physical, social, and emotional ability. (need to know), aesthetic needs (need for beauty), social (need to be among others), and emotional (need for success and mental well being).
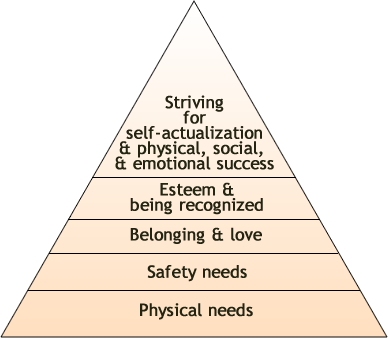
Categories of mental / emotional health with examples
Emotional and mental health - is the ability to accept yourself and others as you express and manage emotions from the demands and challenges of everyday life in positive ways. They can be classified into five categories.
- Sense of belonging - are comfortable communicating with family members, peers, friends, teachers, and others who support you.
- Being social
- Respect and advocate for self and others
- Communicate well with others
- Stand up for self and others
- Good social skills
- Sense of purpose - have purposes you value and desire and are able to set and achieve goals in pursuit of those purposes.
- Meaning and purpose for life
- Set and achieve goals
- Use refusal skills when presented with alternate goals counter to your personal goals
- Positive outlook - Optimistic, see the good and believe success is achievable.
- Being positive.
- Have happy and positive feelings
- Look for the good.
- Self-sufficient or self-efficacy - believe you are capable and able to achieve success.
- Competence - having the ability and skill to achieve success
- Critical thinking and make good decisions
- Use self-talk to motivate and achieve
- Take care of yourself - sleep, eat healthy with good nutrition, exercise, water, personal hygiene, bath, dental care, hair care.
- Avoid high risk behaviors
- Maintain appropriate weight
- Manage conflict
- Manage stress
- Maintain self-control and avoid anger and resolve conflict
- Relaxation techniques
- Health & dental check-ups
- Moderate use of caffeine
- Don't use tobacco, illegal drugs & use prescription drugs responsibly
- Healthy self-esteem - you value, respect, and feel confident about yourself.
- Self-esteem - how much you value, respect, and feel confident about yourself.
Procedures to Manage Emotions
Recognize your feelings as emotionally related
- Ask why might I feel this way?
- Is this really important for my well being or future?
- Should I wait before responding?
- What could I do to feel better?
- Who might I talk to to feel better or get help?
- Is my reaction a defense mechanism?
- Compensation, make up for mistake or weakness by hard work, giving a gift, or other measures. Over compensation is taking compensation to extremes. Paying double or triple the price.
- Denial, don't recognize something that is obvious to others.
- Projection, attribute or blame your feelings, faults, or mistakes to others.
- Rationalization, create excuses to explain a behavior or situation rather than take responsibility.
- Regression, use a behavior that is recognized as immature rather than dealing with a situation in a more appropriate manner.
- Repression, deny the existence of unpleasant feelings or situation by ignoring it and putting it out of mind. Source
Procedure to Increase Self-esteem, Self-efficacy and Develop a Positive Self Identity
Self-esteem is the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
Ideas related to positive self-esteem
- Be positive
- Focus on what is achievable
- Look at mistakes as opportunities to learn. Can only learn by changing.
- Look to accomplish positive change not perfection
- Replace negative talk with supportive talk
- Be with people you value and respect and who value and respect you.
- Try new things to find new opportunities and talents
- Set goals and plan steps to achieve them
- Regular exercise increases stamina and energy
- Help people
Ideas for positive identify
- Recognize and identify your strengths and weaknesses. Include ideas from each side of the health triangle: social, physical, mental/ emotional.
- Be with people you value and respect and who value, respect, and support you.
- Demonstrate positive values
- Set attainable goals, but don't seek perfection or make it a contest where winning becomes the goal. Improvement is the goal.
- Find something you like and do it often. Relate this to your purpose in life.
- Have a purpose in life
- Help others
Procedure to Manage Fear
- Recognize the emotion as fear.
- Figure out what is causing the fear.
- Decide if the situation is legitimate and what if any cautions need to be taken.
- Remember fear can be healthy... Fear causes us to run out of a burning building.
- Identify what might be done to deal with situations that cause the fear. Most often more familiarity with the situation is helpful, but this requires having to face the fear by studying its attributes or stepping into situations, simulating them and practicing how to deal with them. For example fear of tests can be overcome by working on practice tests to gain skill and confidence. Fear of animals can be overcome by working with someone that is skilled with animals and having them introduce people to a particular animal in a safe and nonthreatening way.
- Create a plan to face and over come your fear.
- Share it with someone you trust.
- Implement the plan
- Evaluate
Procedure to Manage Guilt
- Recognize the emotion as guilt.
- Figure out what is causing the guilt.
- Decide if the situation is legitimate and if you are really responsible.
- Decide if the best action is to forget about it, admit a mistake, apologize, promise to be more thoughtful or careful in the future, or other course of action.
- If you accept responsibility, create a plan to communicate your responsibility, remorse and any future actions as appropriate.
- Share it with someone you trust.
- Implement the plan
- Evaluate
Procedure to Manage Anger
- Recognize the emotion as anger.
- Figure out what is causing the anger.
- Take action to calm down. Breathe, say calming words, relax your muscles, walk away, listen to relaxing music, go for a walk, exercise, jog, write in a journal, play an instrument, seek help.
- Decide if the situation is legitimate and if you are really responsible.
- Decide if the best action is to forget about it, admit it was your responsibility for becoming angry. You may have over reacted, taken the situation differently than what was meant, or other miscommunication. Decide if an apology is necessary, or a promise to be more thoughtful or careful in the future, or other course of action.
- If you accept responsibility, create a plan to communicate your responsibility, remorse and any future actions as appropriate.
- Share it with someone you trust.
- Implement the plan
- Evaluate
Procedure to Manage and Deal with Stressful Situations
- Recognize feelings and emotions which are stress related. See below: Bodily responses to alarm, stress, and chronic stress
- Figure out what is causing the stress.
- Remember stress can have both positive and negative results and can be reduced by taking charge, changing or accept perceptions, communication, laughter, exercise is also important to reduce the harmful effects of stress and blow off steam, relaxation techniques .... For more information see Ways to Manage and Reduce stress
- Devise a plan to deal with stress. See ideas below on Ways to Manage and Reduce stress for ideas.
- Share it with someone you trust.
- Implement the plan
- Evaluate
Procedure for Refusal Skills or or how to deal with avoiding something that isn't beneficial or do not what to participate in. See also ways to say no
- Decide to refuse an offer or walk away from ...
- Take a solid stance, look at the person, and use a calm tone.
- Thank them for wanting to include you.
- Give a reason, excuse, assertive no
Examples: - Examples of reasons and excuses
- May want to offer an explanation for why you do not want to participate.
- I have plans to ...
- I don't think it would be good to ...
- Call it what it is. It is against the rules, It wouldn't be fair. I don't do that.
- Change the subject or idea to something else.
- Ask questions. What do you want me to do? Why would you want to do that? How would that benefit me, us?
- Give reasons. I don't need the aggravation. I don't need any trouble. I think differently. If I did that I would feel bad about it.
- Use humor or sarcasm. Sure, that's all I need to do, I'd be grounded for weeks!
- Suggest doing something else. Let's walk. Let's play a game.
- Leave it open. If you decide to do something different, let me know. I'll be home if you want to play video games.
- Use I statements: I statements have three parts:
- A description of the condition to refuse .
- An expression of how you feel.
- A statement of the reason for the feeling.
Examples:
- When I play basketball, I do not enjoy it, because I haven't played it much and am not very good.
- When we goof around, I worry, because we will not learn, get our work done and look bad when we present to the class.
- When we hang out with them, I worry about fitting in and get upset, when JJ makes fun of me.
- Say no
- Nah. No, thanks.
- Thanks, but no thanks.
- Not now (today, tonight, ever ... )
- I have plans to ...
- Offer an alternative activity if you desire.
- Watch a video at ...
- Go get something to eat ...
- Go for a walk or another public place: gym, bowling, dance, music, ...)
- If necessary continue to refuse to participate.
- I said, no.
- I don’t feel like it.
- I really mean no. or repeatedly say no (Broken record).
- Leave ... Walk away (I’ve got to go now. My friends are expecting me in ten minutes).
Refusal can make you empowered and feel good. People who do not honor other's right to make an assertive response are not friends, they want to control others. Source
Coping with loss and grief
Five Stages of grief or loss
Example: cell phone loss.
- Denial or shock difficult to believe or refuse to believe the loss has happened.
You drop your cell phone and turn it on. It doesn't come on. You turn it off and try it again. And again... You deny or refuse to believe it won't start. - Anger, depression, pain, guilt, reflection, remorse
Ah!!! I should have put it in my pocket... stupid, stupid, argh.... I should have ... Stupid me... Why don't I think better? Why am I lazy? Dumb...
- Bargaining make this not happen and ...
Come on turn on and I will take better care of you....
Maybe if I shake it ... - Depression and loneliness
Ugh! What am I going to do. I can't live with out a cell phone.
I won't be able to text my friends.
I will lose them and be alone.... What the ...
- The upward turn, reconstruction, acceptance, and hope
OK. It's dead. Guess that is why I got the insurance. Or
OK it's dead. I don't want to go without one so I will need to deal with my parents.
They will be mad and tell me I am irresponsible, but it really was an accident. Accident or not... Ah! I need to face the music.
OK. that was bad, but it had to be done. I will survive and go on.
I am at peace now and am ready to move on.
Acceptance of loss and grief is not a trivial thing. In fact, we all go through this process anytime whenever something happens we don't expect or want to happen. A shirt we want to wear and find it is in the washing machine so we have to go with out it. A carton of milk that is sour. A toy breaks. We mess up on a project and have to throw it away and start over. Not getting a score or grade we expect. Not making the starting team. Someone sits where we were going to sit. A friend moves to a new town. A friend doesn't want to be friends any more. The loss of a pet. The loss of a loved one.
Grief is sorrow caused by a death; and mourning is the process of showing grief or sorrow. The process is an experience of pain for the loss, search for a reason of the loss, and a determination to move on.
Focusing on things that can't be changed can only continue to add to the pain. It is helpful to think of the positives:
- Celebrate a person's life with memorials, cards, letters, and ceremonies.
- Recall happy and positive times.
- Empathize with others.
- Let the process take time.
- Be a good listener. If not sure what to say, bob, nod, smile, and lower your eyes.
- May also use I statements to express your feelings. I feel so sad when I visit ... , because I will not see ... again.
Dealing with Anxiety and Depression
There is an incremental relationship between feelings of:
excited anticipation - concern - nervousness - stress - anxiety - depression.
It is important to understand this incremental relationship is likely the result of the same neurological emotional functions only varying in the degree of neurochemicals and hormones communication in the body. This supports the need to achieve and maintain a healthy balance between the mind and body for good mental health. Achieving this by managing stress and anxiety before becoming unhealthy.
Anxiety is the condition of feeling uneasy or worried about what might happen.
Anxiety disorder is the emotional feelings caused by real or imagined fears which are difficult to control and can cause a person to withdraw from activity, seek isolation, and develop physical illness, headaches, high blood pressure, and stomach disorders. It is the most common mental disorder.
Feelings of self-consciousness, worry, insecurity, and fear are common when they are infrequent and can be overcome by continuing with a normal life.
However, having muscle tension, continual distractions, not being able to focus, loss of appetite, headache, stomach ache, and not being able to sleep can be associated with an anxiety disorder and if the feelings are prolonged and become feelings of helplessness, hopelessness, sadness, despair, apathy, and discouragement, then it may be depression or an anxiety disorder.
Possible Causes
Not having the lower levels of Maslow's needs met contribute to poor physical, social, and psychological health, which prolonged can cause anxiety and depression. Heredity can contribute by inheriting genes that contribute to higher of lower levels of hormone production than necessary for healthy functioning. This will contribute to internal psychological causes which will interact with external contributions like traumatic experiences, violent neighborhoods, poverty, family relationships, peer relationships, school, and other environmental factors in unhealthy ways.
Management techniques
Methods and strategies used to manage, and reduce stress can be used to reduce anxiety, occasional stress, and mild depression. While chronic stress and depression needs professional medical help.
Methods and strategies that are helpful increase positive thinking and help people to focus and concentrate so they can be productive. Success and productivity that creates feelings of happiness, pleasure, joy, interest, caring, power, and self-fulfillment. Instead of sadness, apathy, irritability, and anger.
Methods that create positive behaviors of self-efficacy, caring, worth, and achievement rather than, neglect of personal needs, not exercising, neglect basic hygiene needs, eating too much or not enough, not sleeping or lying around all the time.
Anxieties include phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, post-traumatic stress Disorder (PTSD), generalized anxiety disorder, eating disorders, kleptomania, cutting, pyromania, excessive gambling, compulsive shopping.
If a person isn't having success by trying to manage their anxiety and depression, they need to get professional help.
Suicide Prevention and Getting Help
Suicide is the intentional taking of one's own life. It is the second or third leading cause of death for teens and young adults, according to various sources.
Anticipatory excitement - concern - nervousness - stress - chronic stress - anxiety - angst - depression - suicidal thoughts
The relationship of these feelings is important as they seem related and stress and depression are related to suicide. Stress and depression exist in various degrees and ways before a suicide attempt. There are warning, however, they are unique to individuals and not everyone who is suicidal will experience depression or display all the warning signs.
Warning signs
- Stress and depression exist to different degrees
- Withdrawal from family and peers
- Loss of interest in previously pleasurable activities
- Poor school work or poor quality of participation in other activities
- Difficulty concentrating on schoolwork
- Persistent boredom and not caring
- Neglect of personal appearance
- Obvious changes in personality
- Sadness and hopelessness
- Changes in eating patterns, such as sudden weight loss or gain
- Changes in sleep patterns general lethargy or lack of energy
- Symptoms of clinical depression
- Violent actions, rebellion, or running away
- Drug and alcohol use
- Symptoms that related to emotional state (e.g., headaches, fatigue, stomach aches)
- Loss of ability to tolerate praise or rewards
- Giving away personal items
- Frequent talking or writing about death, wishing for death, threat of suicide, or indirect statements about not being able to go on...
Helping
- Initiate a meaningful conversation
- Knowing the majority of suicide survivors regret their decision to attempt suicide may be helpful information
- Show support and ask questions
- Persuade them to seek help
- Text them or pass them a slip of paper with a help line phone number or web site URL
- Talk to someone else, parent, teacher, counselor
Getting help
- Getting help is a sign of inner strength.
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline 1-800-273-TALK or visit their Web site.
The National Suicide Prevention Lifeline's mission is to provide immediate assistance to individuals in suicidal crisis by connecting them to the nearest available suicide prevention and mental health service provider through a toll-free telephone number: 1-800-273-TALK (8255). It is the only national suicide prevention and intervention telephone resource funded by the Federal Government.
Teen Stressors
1. School:
- Grades/GPA
- Events, tests, presentations, contests, games, concerts,
- College
- School regimentation and standardization that doesn’t embrace teens’ strengths, values or creativity
2. Family & Parents:
- Unrealistic high expectations and pressure to do well
- Not achieving/ blowing it for parents
- Out of love, parents want teens to succeed in everything. While this idea is nice, it’s really an unrealistic expectation.
- Stressed parents transfer stress to their teens.
- Lack of positive attention
- Abuse
- Working after school and in the summer
- Family obligations: chores, taking care of siblings, fixing meals, housekeeping ...
3. Peer group & social
- Not getting along with friends
- Worrying about fitting in, personal appearance, ...
- Busy schedule with peer demands to
- Boyfriends/Girlfriends relationships
- Bullying
- Moving
- Extracurricular activities: sports, band, choir, art, dance, shows, try outs
- Sex
- Pressure to smoke
- Pressure to use alcohol and other drugs
- Sexual harassment
- Puberty
4. Life skill
- No time: lack of time management skills: budgeting time, meeting deadlines, keeping up
- Getting appropriate amount of sleep
- Doing two things at once
- Too much going on
- Being prepared
- Occupational tension
5. Physical and mental/ emotional
- Personal thoughts, self-esteem, self-efficacy,
- Infection, disease,
- Changes in body, personal appearance: body size, weight, muscularity, ...
- Unsafe neighborhood or community
- Media reports (TV, video feeds, Internet, newspapers, magazines, ...)
- Noise
- Tension, anxiety,
- Use of salt, alcohol, other drugs, chemicals, and environmental toxins
- Insufficient sleep and irregular day or night rhythms
- Extreme climate or hight altitude
- Violence and war
- Global warming
- Illness
- Grief and loss
- Injury, accidents
Bodily Responses to alarm, stress, and chronic stress
When you are threatened, startled, or alarmed your body immediately starts a series of internal changes, referred to as the fight-flight-or-hide response. This response is triggered when the sensory cortex interprets an alarm situation and the hippocampus in the (temporal lobe) relates the present situation to memories of previous times, places and situations.
If a dangerous situation is sensed, connections through the insular cortex, between brain areas of the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex fine tunes a safe response and activates two pathways: the sympathomedullary (SAM) and the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) pathway to activate the response. These pathways are part of the endocrine, nervous, and immune systems that work together to communicate to the rest of the body to release hormones to achieve a safe and healthy response.
In the short term the hypothalamums starts the sympathomedullary (SAM) pathway by sending signals through nerves to the adrenal glands which release the famed, adrenaline (also known as epinephrine, which causes constriction of blood vessels and use of glycogen) and norepinephrine (regulates blood vessel tension and use of glycogen)
Adrenaline flow through the blood stream and causes a fight-flight-or-hide response. It increases the heart rate and constricts blood vessels for faster blood circulation, increases breathing for oxygen, raises glucose and lipids levels in the blood for energy, dilates the pupils for better observation, raises hairs on your body to look bigger, starts carbohydrate metabolism to prepare the muscles for exertion, and increases secretion of sweat and saliva to regulate temperature. Muscles start to tense and shake and release their stored up ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for energy and strength, which explains the stories we have all heard about people performing amazing feats of strength, or how they have continued to operate after being shot, stabbed, or maimed.
If the threat continues the hypothalamus (in the brain stem) sends corticotropin releasing hormone (CHR) to the pituitary (below thalamus) and starts the HPA paathway. Then the pituitary gland, secretes andrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) to the adrenal gland, (in the kidneys) which releases the hormone cortisol. The hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) pathway can keep the body on high alert by continuing to release cortisol into the bloodstream, which increases the use of glucose and reduces nonessential functions. If the body feels the treat has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) will relax and replenish the body.
Of course, after a heroic feat the body will have used a massive amount of energy and resources and require serious recovery time, referred to as a rest and digest response.
While most people don't experience situations that bring on full blown alarming fight-flight-or-hide responses, they do experience situations of stress, anxiety, and fear, which cause the releases of these hormones, in lesser amounts, into the bloodstream. A certain amount of each hormone is necessary for good health, however, as the amounts increase beyond the range for a healthy balance, they can cause negative effects and disease. This condition is chronic stress and continued elevated amounts of adrenaline and cortisol in the blood stream is an indicator of chronic stress, which has negative effects on the health of the body and its immune system. See health: anatomy - nervous system
Chronic stress
Chronic stress affects the hippocampus (involved with memory), amygdala (involved with emotional stability), and pre-frontal cortex (PFC - involved with attention, planning, and follow-through).
- A faulty hippocampus means you might not remember that the guy at bat likes to hit down the right field line, so you forget to cover the line when you're playing right field.
- A sub-par amygdala means you might go ballistic when a call doesn't go your way, and you get ejected from the game.
- When your PFC (pre-frontal cortex) is drained of energy, you tend to lose focus and zone out, so you can't meet expectations.
Chronic stress also weakens your body's immune system, making it more likely that you get colds, flu bugs and other infections during emotionally difficult times, cardiovascular disease, anxiety, and depression Stress associated with extreme events can lead to post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) which can include flashbacks and hypervigilance. Stress can also cause people to engage in impulsive behviors and substance abuse.
Stress can be controlled with relaxation techniques like deep-breathing and meditation to pump up your brainpower and your athletic performance.
Ways to Manage and Reduce stress
See also Procedure for stressful situations
Our distant ancestors evolved three options, fight, flight, or hide, (collectively known as, fight-or-flight) to deal with threats in their environments. Today, stress, also results from situations that are not life threatening, but are interpreted with our outdated emotional system. While these three options may work when dealing with wild animals, they are not the best choices for all the threatening situations that arise in today's world.
However, when stressed these three options instinctively come to mind, but for most situations there are most likely better choices.
Choices beyond 1. fight, 2. flee, 3. hide (fight-or-flight) that may move to rest, digest, and recovery, include:
- Take charge and accept the situation or look at it as a problem to be solved, an opportunity for change or a learning situation. Don't be afraid to manage the situation by reducing the task or the level of performance. Don't let perfection be the driving force. Listen to TED Talk.
Emotions create feelings. Stress is related to feelings of being overwhelmed, frustrated, angry, distracted, impatient, scared, and worried. However, once these negative feelings and their causes are recognized, they can be reduced and replaced when a person uses take charge actions and gains control of the situation. By being resilient and challenging themselves to accept the situation and move forward, or to accept it as a problem that can be solved. A situation or problem that can be looked at with wonder and amazement as a new adventure to explore. An exploration, that with sufficient effort and strategies will provide discoveries of new ideas and alternative ways to accept and turn problems into opportunities. - Be kind to yourself. Forgive yourself for anything that didn’t go well and if you need to apologize or take responsibility in some way, then do it and move on. Remember the five stages of grief when it seems impossible to let go.
- Use self-talk for encouragement with all of the strategies. I know I can do this. I have done this before. This is new and will be exciting and a great opportunity.
Turn anxiety about new situations with self talk like: it will be exciting and a great opportunity. Reframe negative talk by looking for opportunities, make a positive idea, and focus on it. If can’t make it positive, then try to make it neutral. Instead of focusing on the whole situation focus on some part of the situation and make it positive. Maybe how you will do it. What you wear at the time, what you take with you, what you use, who you will meet, or any small part of the bigger related situation. For example, instead of focusing on the negative about something related to school, class, work, chores, or other situation. Think of something positive about how you could be involved with it. Maybe something you wear to be comfortable or make you happy, choose tools that you would enjoy using, look forward to working or being with someone, imagine being creative in how you could be involved, or imagine finding or making a part of the negative experience a positive situation. - Change or accept another person's perceptions as okay.
Change from seeing the situation as undesirable to seeing it as an opportunity.
Example: Change
Rather than seeing having to give a speech as a stressful situation to be avoided, change and see it as an opportunity to help others learn something you feel is important for them to know.
Example: Accept
A child can accept the parent's point of view that restrictions on a child is necessary to reduce the stress they feel from their perceptions of the dangers the child will face when they leave home and how they believe the restrictions will reduce those dangers.
A parent can accept the child's point of view to reduce the stress the child feels by their perceptions of the restrictions as their parents not trusting them, that they think they are irresponsible, or lack maturity. The parent can accept the child's point of view by discussing how to avoid or what to do in dangerous situations and how to deal with their peers interpretation of the restrictions.
Therefore, stress can be increased or decreased depending on how people feel about it. By sharing different points of view people can communicate their concerns and devise a plan that is less stressful for both. - Communication - Stay connected to family, friends, and significant others. Schedule time to talk or communicate. Remember communication is possible in so many ways and so necessary to maintain healthy relationships. May want to review suggestions for healty relationships which can reduce or increase stress between people or groups of people with and without communication. For example, when people discuss their stressors through open communication they demonstrate to each other they are capable and can be responsible to choose appropriate behaviors. When both do so, they will increase the trust each has for the other and reduce stress. Conversations to assist behavior change can be helpful.
- Time management - planning and scheduling your time, refusing to accept tasks or activities the will cause stress by saying no. Planning ahead so people are prepared and know what to expect is one of the best ways to reduce stress (plan for test, practice for concerts, practice for sporting events, ...).
- Laughter and smiling reduce cortisol, adrenaline, increase endorphins, and reduce blood pressure. It also is said to make you look great, feel great, and appear more competent. TED talk
- Exercise is also important to reduce the harmful effects of stress and blow off steam. See more information on exercise, hormones, and stress below. See also information on setting goals and planning a physical activity program.
- Relaxation techniques.
- Listen to relaxing music.
- Take a hot bath with Epsom salts before bed.
- Use essential oils, like lavender.
- Message. Swedish massage increases the level of oxygen in the blood, decreases muscle toxins, improves circulation and flexibility while easing tension. A study published in The New York Times, found a Swedish massage decreases cortisol, increased lymphocytes, white blood cells that help fight infections, colds, and flu. A foot massage (aka foot reflexology) also reduces stress. When cortisol levels are up, you can be certain too much energy has gone into your head.
- Make a list of all the things you are grateful for Oprah Winfrey calls it her gratitude journal.
- Meditate. 1. The act or process of spending time in quiet thought. 2. Spend time in quiet thought for religious purposes or relaxation. Source Merriam-Webster. Mindful relaxation that defines purpose, goals, acceptance, love, or other positive emotions that can reduce cortisol levels and hence stress.
- Develop a procedure that will allow you to relax.
Relaxation procedure
Move parts of your body from your head to your toes or your toes to your head and breathe slowly and deeply (from your abdomen not the top of your chest) as you do.
For example you could sit or stand. Start by stretching, then lean back and extend your arms and legs, stretch them and slowly rotate arms and legs. Then add wiggling of your fingers and toes. Then you might sway your body forward and back or right to left stretching muscles from the top of your body, to your arms, then your abdomen, legs, ankles, and toes. You could create a similar procedure for standing.
If you don't think you are getting enough circulation you could wiggle your fingers on each hand in a waving pattern and begin touching them quickly one at a time on the top your head, like rain drops falling on the top of your head. Then slowly move the tapping around the top of you head, around on your sinuses, cheeks, jaw, chin, neck, shoulders, collar bone, arms, sides, stomach, hips, thighs, legs ankles and feet. As you do, keep swaying to stretch your muscles.
Also during the stretching and rain drops remember to breathe slowly and deeply (from your abdomen not the top of your chest), holding it for awhile and exhaling slowly.
Then you can add self-talk by saying something like:
Even though I was expecting to .... and will not get to ...
I accept it.
I love and accept myself.
I accept how I feel about it.
I am calm and relaxed about it.
This anxiety in my body is ... and it feels ... and I will control it.
I love and accept myself.
I release all the anxieties I feel.
I acknowledging it and rather than spend so much time denying it or wishing it wouldn't happen as ...
I allow it...
I allow myself to release the fear and anxiety it creates.
I know what it feels like to feel calm.
I feel the calm returning as I allow myself to move on.
Think calm relaxing thoughts and continue one more cycle of you relaxation exercise routine. - Sleep
- Get eight hours of sleep
- Follow a nightly routine
- Be consistent about the time you go to bed and get up.
- Unplug from electronic devices. Especially in the evening to sleep better.
- Read
- Darken the room. If your eyes are exposed to light your pineal gland (in your brain) will not secrete melatonin needed for a good night's sleep.
- Volunteer - Caring creates resilience and belonging.
- Diet - see nutrition information
- Eat protein rich seeds and other high quality proteins you digest well. Research suggests lower protein levels will chronically increase cortisol levels.
- Eat quality unrefined fats - Omega 3 fatty acids lowers cortisol and the inflammation it causes.
- Research and find herbs like Tulsi or Holy Basil that lowers elevated cortisol and regulate blood sugar.
- Minerals are necessary for the adrenal glands to provide you with energy. A varied diet will provide these.
- Limit caffeine (adults to 4 cups or less), stop caffeine after 2 PM, best to use caffeine before exercising. Increased caffeine can create a buzz, continued consumption turns to anxiety, and more can cause an overdose, which is dangerous and can cause death.
- Combine ideas from above. Take charge, use self-talk, accept the situation, communicate with yourself, exercise, and relax.
Exercise, hormones, and stress
Introduction
We all know exercise is healthy. It helps retain and build muscles, endurance, reduces stress, improves circulation, and improves over all emotional well being. However, how does exercise affect stress and well being?
All the substances and hormones the body needs are transported through out the body. Exercise increases circulation throughout the body and better circulation improves the efficiency of transportation of materials throughout the body. Therefore, there is a positive relationship between exercise to support circulation as well as other benefits of exercise.
Mostly when people think of circulation, they think of transporting blood and moving what their bodies need. What we eat and drink: nutrients (protein, sugar, fat, and carb molecules) vitamins, water, amino acids; and what we breathe: oxygen. Then, the may include carbon dioxide, liquid and solid waste, toxins, antibodies, bacteria, and hormones.
While the transportation of all of these is important, it is the transportation of hormones that communicate between the physical body and the brain's neurological functions that regulate stress. A stressful event causes secretion of adrenaline and increases the levels of adrenaline in the blood stream within two to three minutes of a stressful event. When the stressful situation ends, the adrenal glands stop producing adrenaline. Therefore, the idea that it is possible to not let yourself be stressed has merit if a person can stop being alarmed by a situation before two to three minutes pass or as soon as possible.
There are many ways to achieve this, which is known as, stress management or ways to reduce stress. The purpose is to move from a stressful situation toward a relaxed state, which is sometimes referred to as, rest, digest, and recovery. Stress and relaxation physically affect a person in these ways:
- Hormonal balance changes in positive ways with reward, laughter and meditation. In situations that cause these feelings hormones are released that create enjoyment, and over all good feelings. Situations that cause fear and worry increase hormones that cause stress, aggression, withdrawal, and avoidance. Actions like meditation, sleep, rest, or time without stimulation will decrease hormonal effects as well as drinking water or being hydrated.
- Activity changes the transportation rate of materials being moved around the body from place to place (faster or slower). Exercise and rest effect hormone production, blood circulation, and breathing rate, which determines if the needs of the cells, tissues, and organs are being met for their optimal performance.
- Rate of transportation is also determined by the size and tension of blood vessels and the viscosity of the blood, which is determined by exercise, hormones, medication, and water.
Better communication provides more neurochemicals in a timely manner for better brain - body communication. This improves health as the body is better able to function by sending, receiving, and responding to signals, such as stress. If enough energy and sufficient nutrients are available the body will regulate, repair, and grow efficiently (homeostasis).
To regulate stress the brain neurological functions communicate with all cells, organs, and systems through the nervous, cardiovascular, and endocrine system. To be relaxed and calm it must communicate a healthy balance of chemicals, nutrients, and water. Therefore, communication may be the true value of exercise. The less we exercise the less efficient our bodies are in responding to changes, particularly stress.
Hormones and other substances related to stress, rest, and recovery
- Water Blood flow and regulation improves with sufficient amounts of water. Cerebral brain functions are improved with sufficient amounts of water. however, it is also possible to drink too much water. To replace water loss from sweating while exercising or other types of physical exertion, adults should drink 1.5 to 2.5 extra cups of water: depending on the temperature, altitude, their size, and time exercising. Since sodium is also lost through sweat, they may want to substitute a sports drink with sodium for some of the water.
- Adrenaline see epinephrine causes constriction of blood vessels, tension of blood vessels and use of glycogen.
- Aldosterone regulates sodium excretion important to maintain electrolyte balance.
- Cortisol is know as the chronic (long term) stress hormone, though there are others. The release of adrenocorticotropic hormone from the pituitary gland promotes the production and secretion of cortisol from the adrenal cortex. It maintains blood glucose for long periods of exercise by signaling the body to start breaking down proteins and triglycerides. Excessive physical activity and exercise without providing sufficient time to rest will increase cortisol, which is associated with inflammation, lowered immunity, reduced short-term memory, constipation, weight gain especially in the abdominal region, loss of muscle tone, osteoporosis, and reduced production of hormones: growth hormone, testosterone, DHEA and estrogen.
- Dopamine and serotonin are pleasure chemicals responsible for happiness, restful sleep, and a healthy appetite. More serotonin means more energy and clearer thinking. Exercise increases these and smiling, even forced, can cause feelings of happiness.
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter released as part of the brain’s reward system. When released it gives a feeling of pleasure.
- Serotonin is a neurotransmitter to balance mood and feeling satisfied, well being and reward.
- Endorphins originate in the pituitary gland. Make you feel exhilarated, happy, and block pain.
- Epinephrine, adrenaline, increases metabolism which will also increase the use of fat and sugar for energy, but will also burn muscle in the absence of sufficient sugar and fat stores. The production increases proportional to increased exercise intensity and duration.
- Estrogen determines if carbs or fat are used to fuel the body during an intense exercise session. Women tend to burn fat for fuel because they have higher levels or estrogen, while men tend to burn carbs.
- Growth factors are similar to hormones. Growth factors hepatocyte, fibroblast, and insulin like growth factor (IGF 1) sends signals to satellite cells to regulate the repair, rebuilding, and growth of muscle mass. IGF-1, for example, signals new muscle cells to fuse to existing muscle fibers to repair muscle cells damaged by exercise.
- Growth hormone is a complex chain of amino acids secreted by your anterior pituitary gland. It is needed for muscle growth, collagen repair, joint health, immune system function, and healthy skin. Requires intense training and short rest intervals. Lifting or exercising to exhaustion increased growth hormone levels 200%. Just be careful and use a spotter.
- Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas and regulates blood sugar levels. More insulin decreases blood sugar faster. After a hard work out blood sugar is low and insulin levels high. To reduce insulin levels after a workout take simple sugars or simple proteins, such as dextrose and whey.
- Neurohormones like norepinephrine, improves cognitive function dulled by stress by elevating mood and learning, whose production is increased with exercise. Exercise can make you smarter.
- Oxytocin - released by the pituitary gland in stressful situations. Urges you to seek others for support and help, promotes bonding and helping others, provides anti inflammation effects, helps regenerate and strengthen heart cells. In women during birth it stimulates the contraction of the uterus and production of breast milk. It cements a bond between mother and child. Seems to increase social information processed in the brain.
- Blood sugar is the amount of glucose or other sugars available in the blood stream for energy. See nutrients that provide energy. Low blood sugar increases adrenaline. Therefore, it is important to eat foods that release energy over a longer period of time, like fruit, meat, cheese, and nuts, rather than sugary candy.
- Testosterone contributes to muscle repair, building, and growth in both men and women. Requires intense exercise.
- Thyroid hormones are made in the thyroid and control metabolism.
- Thyroxine, or T4, increases metabolism and hence caloric use during exercise. This will allow the body to burn off excess sugar and fat faster. However, if you lack sufficient sugar or fat to burn, your body will begin to use muscle for energy and result in the lose muscle mass.
- Vasopressin is released by the brain and regulates the amount of water in the blood stream. Related to sweat when you exercise, staying hydrated, and urine production.
Immunity and exercise
How exercise increases immunity:
- Exercise stresses the body and makes a more effective immune system. Stress causes positive changes in antibodies and white blood cells so they fight disease more effectively.
- Exercise increases circulation and moves necessary antibodies and nutrients, water, oxygen farther and faster and removes waste better. Rapid movement will help detect illnesses earlier, than if no exercise, and provide for a faster and better response.
- Physical activity can help flush bacteria out of the lungs and airways and reduce the chance of getting a cold, flu, or other airborne illness.
- Increase in body temperature during and right after exercise can prevent or slow bacteria growth as what might happen with a fever.
- Exercise slows the release of stress-related hormones. Lower stress hormones protects against illness. See stress and exercise.
Caffeine and hormones
- Adenosine - Calms the body by slowing neural activity, allowing relaxation, rest, and sleep. Caffeine inhibits its absorption, which will cause short term alertness, but can cause sleep problems later.
- Adrenaline - Caffeine increases adrenaline which gives a temporary boost, but can tire and depress you later. People tend to drink more to over come this, but doing so will cause sleep problems later.
- Cortisol - Caffeine increase the cortisol, which cause various problems: weight gain, moodiness, heart disease, and diabetes.
- Dopamine - Caffeine increases dopamine, which can make you feel good, but after it wears off you can feel low, which can lead to dependence.
Accurate and quality information is needed to make good decisions.
A healthy person understanding what is human, their body, it's anatomy, functions of life, growth, and development well enough to care for them self and others to attain and maintain physically, emotionally, and socially healthy bodies. To achieve this one must be able to describe, analyze, predict, and compare how different variables affect the body to make wise decisions. Desire to learn about nutrition diet, exercise, sleep, stress, relaxation, choice of behaviors, social skills, conflict resolution, cooperation, genetics, safety, injuries, health status, illness, natural disasters, environmental health, and risks, will impact them and others in different situations or conditions.
Word bank
Alienation is a feeling of being isolated and separated from people.
Anger a strong feeling of annoyance, displeasure, rage, fury, or hostility
Anorexia nervosa is a mental and physical disorder characterized by loss of weight brought on by an unrealistic fear of weight gain, self-starvation, and conspicuous distortion of body image. Health is compromised and may be fatal. Latin definition means - nervous inability to eat.
Anxiety is a feeling of unease, stress, or worry about what might happen.
Anxiety disorder is the most common mental disorder. It is the emotional feelings caused by real or imagined fears which are difficult to control and can cause a person to withdraw from activity, seek isolation, and develop physical illness, headaches, high blood pressure, and stomach disorders.
Apathy is a feeling associate with the loss of hope, lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern.
Behavior the way a person acts, usually in response to a particular situtation or stimulus.
Behavioral therapy is treatment behavioral problems with the focuses on changing behavior with reinforcement (reward, punishment, time-out).
Bulimia nervosa is a mental and physical disorder characterized by consumption of large amounts of food (binge) and ridding of the food and calories (purge) by fasting, excessive exercise, vomiting, or using laxatives. The behavior often serves to reduce stress and relieve anxiety created by concern with weight and self-image. It is often accompanied by depression, is serious and sometimes life-threatening.
Character is the combined qualities that describe how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
Chronic stress is indicated by continued elevated amounts of adrenaline and cortisol in the blood stream which has negative effects on the health of the body and its immune system. It is caused by conditions that are beyond a person's control.
Cluster suicides is a term used to describe a series of suicides that happen in a short period of time in the same geographical area.
Competence is the skill and ability to do something.
Compulsive shopping is spending money to buy stuff that is not needed or not being able to pay for what is bought.
Conduct disorders is when behavior interferes with the rights of others or basic rules of conduct. For example stealing, lying, aggression, violence, truancy, arson, or vandalism.
Constructive criticism is non-hostile comments that suggest a problem, assist in resolving it, and encourage positive change.
Coping is dealing successfully with changes in life.
Counselor is a professional trained to give guidance on personal, social, or psychological problems.
Cutting disorder is cutting the body for pleasure.
Defense mechanisms are mental processes used to protect us from strong feelings and stressful emotions. Examples
Depression is a mental state or prolonged feelings of helplessness, hopelessness, sadness, despair, apathy, and discouragement. Different than grief, which is caused by a real personal loss.
Drug therapy is the use of drugs to treat medical disorders.
Drug addiction therapy is discussion and interventions with professionals intended to guide and help addicted individuals stop compulsive drug use.
Emotional health is a state of mental well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. To be able to cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
Emotions are signals that effect how you feel and can consciously an unconsciously cause body reactions and behaviors.
Empathy is the ability to imagine and understand how someone else feels.
Family therapy is when family members meets with a professional therapist to learn how to communicate better, understand each other, and seek solutions for problems in positive ways that bring the family together rather than tear them apart.
Fear an unpleasant feeling caused by an emotional reaction to a belief that someone or something is dangerous and could cause pain, a threat, serious injury or death.
Gambling disorder is continual gambling with excessive losses.
Group therapy is when a group of people with a similar situation or problem meet regularly with a professional therapist to discuss ways to cope and live happy and productive lives.
Grief a strong feeling of sorrow, misery, sadness, anguish, pain, heartache, heartbreak, agony, or torment over loss.
Guilt an emotional reaction of wrong doing or regret, imagined or real, for failing to be responsible or for committing an offense, crime, or wrong.
Hormones are chemicals produced by your glands that regulate bodily actions and cell behaviors.
Hostility is the intentional use of unfriendly or offensive behaviors.
Influence is a power within ourselves that is strongly affected from outside, social and physical objects. Influences are real and very powerful. They can be very hard to recognize and make it difficult to make good decisions. Influences affect decision making and can be represented by influence systems and circles of influence on people.
Integrity is sticking to core ethical values.
Kleptomania is unplanned stealing of stuff.
Mental disorders are illnesses of the mind that affect the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of people and prevents them from leading happy, healthful, and productive lives.
Mental health is a state of emotional well-being that enables a person to set and achieve their personal goals. To be able to cope with stress, meet challenges, solve problems, and contribute to society in an environmentally healthy way.
Mood disorders are illness with emotional extremes that interfere with everyday life. They include depression, bipolar, or manic-depressive.
Mourning is the act of showing sorrow, regret, and grief when someone dies.
Needs things necessary for a particular purpose. Needs for survival and health, like Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
Neurologist a doctor who specializes in the the brain, nerves, and nervous system.
Obsessive compulsive disorder is when a person is persistently (obsessive) driven (compulsive) by anxiety or fear to repeat a behavior over and over. Fear of germs, wash hands or use sanitizers...
Panic disorder is a sudden unexplained feeling of fear and terror. It can cause shaking, increased heart beat, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Perception the process of becoming aware of information with your senses (eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue)
Personal identity is a person's sense of them self as a unique individual.
Personality is a complex set of characteristics that make a person unique.
Phobia is an irrational fear of something specific such as snakes, height, or social occasions.
Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can happen after experiencing a terrifying event symptoms such as flashbacks, reliving the event, nightmares, guilt, reduced involvement with others, lack of emotional feelings, sleeplessness, problems focusing and concentrating, hyper alertness, and exaggerated startle response.
Psychiatrist is a medical doctor who specializes in the mental disorders and can prescribe mediation.
Psychosomatic response is a physical reaction that results from a mental factor such as mental conflict or stress not from a physical illness or injury. Headache, weakened immune system, high blood pressure, digestive disorders, teeth gnashing...
Psychotherapy is the treatment of mental disorders with an ongoing discussion to find a cause and solution for a problem rather than by medical means alone.
Pyromania is setting fires for pleasure.
Resilient ability to adapt and recover from disappointment, set-backs, crisis, or other goal blocking situations.
Role model is a person whose success and behavior is emulated.
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder where a person has delusions, hallucinations, or other loses of contact with reality.
School Psychologist is a professional who specializes in the study of emotional, mental, and social, aspects of school aged students and the effects they have on student learning and behavior.
Self-actualization is being able to achieve success
Self-efficacy is the belief in your ability to learn, change, accomplish success or failure
Self-esteem is the value, respect, and confidence you have for yourself.
Self-management is the decisions a person makes about diet, exercise, safety, first aid, seat belt usage, cell phone use, texting and driving, alcohol, medicine use, drug use, risk management, and any other behavioral choice that affects a person's health and wellness.
Compulsive shopping is spending money to buy stuff that is not needed or not being able to pay for what is bought.
Social emotional learning (SEL) is the proces, knowledge, attitudes, and skill we learn and use effectively to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions.
Stages of grief are the reactions a person may have when they experience a loss. They may be in a particular order or not. See five stages of loss and grief below.
State of mind is a person's mood influenced by their conscious and unconscious thoughts about them self and the outside world that affects the choices they make and their behaviors.
Stress is the reaction of the body and mind to everyday opportunities, challenges, and demands.
Stressor is something that cause stress.
Stigma is a mark or feeling of shame or disapproval that results from being isolated, shunned, or rejected by others.
Suicide is the intentional taking of one's own life.
Traumatic event is a sudden and shocking situation that overwhelms all normal coping strategies that provided confidence and security. Accidents, natural disasters, violent assaults, suicides.
Values ideas, beliefs, and attitudes a person holds precious and use to guide their life.
References
- TED talk The Hidden Power of Smiling
- TED Talk How to Make Stress Your Friend